The chain mediating role of family health and physical activity in the relationship between life satisfaction and health-promoting lifestyles among young adults in China
- PMID: 39296851
- PMCID: PMC11408350
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1408988
The chain mediating role of family health and physical activity in the relationship between life satisfaction and health-promoting lifestyles among young adults in China
Abstract
Background: Unhealthy lifestyles during adolescence are significant factors leading to chronic diseases in the future. Enhancing health-promoting lifestyles among young adults in China is crucial for preventing and reducing the risk factors of chronic diseases.
Objective: This study aims to explore the relationships between life satisfaction, family health, physical activity, and health-promoting lifestyles among young adults in China. It also seeks to confirm the chain mediation role of family health and physical activity in the influence of life satisfaction on health-promoting lifestyles in this population.
Methods: This study, conducted from August 2023 to November 2023, employed a random sampling method to recruit young adult participants aged 18-40 in the southwestern region of China. Variables were measured using the Satisfaction with Life Scale (SWLS), the Family Health Scale-Short Form (FHS-SF), the Physical Activity Rating Scale-3 (PARS-3), and the Health-Promoting Lifestyle Profile II Revised (HPLP-IIR). Data analysis was performed using SPSS 27.0 and the PROCESS macro version 4.1.
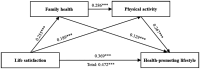
Results: The results indicated that life satisfaction was positively correlated with family health (r = 0.225), physical activity (r = 0.245), and health-promoting lifestyles (r = 0.506). Family health was positively correlated with physical activity (r = 0.320) and health-promoting lifestyles (r = 0.312). Physical activity was positively correlated with health-promoting lifestyles (r = 0.429). Additionally, life satisfaction could influence health-promoting lifestyles directly (effect = 0.369) and through three mediation pathways: (a) family health (effect = 0.033); (b) physical activity (effect = 0.050); (c) family health and physical activity (effect = 0.020).
Conclusion: This study supports the mediating role of family health and physical activity in the influence of life satisfaction on health behaviors among young adults in China. Therefore, we recommend that future public health initiatives place greater emphasis on family health and create conditions that facilitate physical activity for this group. This could be an important direction for further enhancing health-promoting lifestyles among young adults in China.
Keywords: China; chain mediation; family health; health-promoting lifestyle; life satisfaction; physical activity; young adult.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Huang, Tian, Liu, Luo, Tao and Peng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health-promoting lifestyle and life satisfaction in full-time employed adults with congenital heart disease: grit as a mediator.Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2024 May 28;23(4):348-357. doi: 10.1093/eurjcn/zvad104. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2024. PMID: 37847800
-
The association between health-promoting-lifestyles, and socioeconomic, family relationships, social support, health-related quality of life among older adults in china: a cross sectional study.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2022 Apr 20;20(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12955-022-01968-0. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2022. PMID: 35443689 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of physical exercise on university students' life satisfaction: The chain mediation effects of general self-efficacy and health literacy.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 9;20(6):e0325835. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325835. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40489508 Free PMC article.
-
Socioecological influencers of health-promoting lifestyles in Chinese: a preliminary survey using convenient samples.Front Public Health. 2024 Jan 8;11:1309824. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1309824. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38259776 Free PMC article.
-
Health-promoting lifestyles and their related influences among nursing assistants in nursing homes in China.Appl Nurs Res. 2018 Feb;39:97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.apnr.2017.11.009. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Appl Nurs Res. 2018. PMID: 29422184
Cited by
-
The independent and joint role of socioeconomic status and family relationships on mortality risk in China: cultural differences and health inequalities in the context of intergenerational cohabitation.Arch Public Health. 2025 Jul 15;83(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s13690-025-01669-2. Arch Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40660323 Free PMC article.
-
The Mediating Effect of Grit in the Relationship Between Middle School Students' Trust in Their Physical Education Teachers and Health-Promoting Behaviors: Evidence from Korea.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Jul 9;13(14):1650. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13141650. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40724675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Y, Chen H, Liu J. Household Split, income, and migrants’ life satisfaction: social problems caused by rapid urbanization in China. Sustain For. (2019) 11:3415. doi: 10.3390/su11123415 - DOI
-
- Xiao C, Silva EA, Zhang C. Nine-nine-six work system and people’s movement patterns: using big data sets to analyse overtime working in Shanghai. Land Use Policy. (2020) 90:104340. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.104340 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous