The effects of folk-dance in schools on physical and mental health for at-risk adolescents: a pilot intervention study
- PMID: 39296856
- PMCID: PMC11408180
- DOI: 10.3389/fspor.2024.1434661
The effects of folk-dance in schools on physical and mental health for at-risk adolescents: a pilot intervention study
Abstract
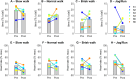
We present the findings from a pilot study to evaluate the effects of a six-week adapted folk-dance intervention on physical and mental health for at-risk adolescents conducted in schools. At-risk adolescents are at particular risk for sedentary behavior, poor mental health, and lower quality of life, and are likely to benefit from motivating and health-promoting activities such as dance. However, it can be challenging to conduct and evaluate evidence-based interventions with this population. We conducted a convergent parallel mixed-method design using pre-post measures of mental well-being, as well as pre-post measures using inertial measurement units to assess physical activity during a 6-week adapted folk-dance intervention. At the completion of the study, we conducted semi-structured interviews with all stakeholder groups. We observed significant improvements in mental well-being, as indicated by increased WEMWBS and MHC-SF scores, while the UCLA score showed no significant change, with these outcomes independent of age and gender. Furthermore, at-risk adolescents reduced the time spent in stationary/resting position, while their heart rates were also reduced by ∼15% in such conditions. Our results suggest that at-risk youth who participated in adapted folk-dance became more enthusiastic and showed more willingness to move over the course of the intervention. Quantitative results were supported by interviews, which found that participants responded positively to the adapted folk-dance classes, and reported both elevated physical exertion and high levels of enjoyment. The mixed-method research design also provided insights into the suitability of data collection methods for this hard-to-reach population. We report on these outcomes, including best practices for working within schools on health-promoting physical activities.
Keywords: arts & health; at-risk adolescents; folk-dance; mental health; physical activity; physical health; well-being.
© 2024 Jochum, Egholm, Oliveira and Jacobsen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health. Geneva: World Health Organzation; (2010). Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK305057/ (accessed May 6, 2024) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

