Unlocking DOE potential by selecting the most appropriate design for rAAV optimization
- PMID: 39296857
- PMCID: PMC11406035
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101329
Unlocking DOE potential by selecting the most appropriate design for rAAV optimization
Abstract
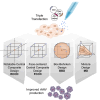
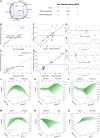
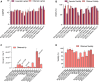
Producing recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) for gene therapy via triple transfection is an intricate process involving many cellular interactions. Each of the different elements encoded in the three required plasmids-pHelper, pRepCap, and pGOI-plays a distinct role, affecting different cellular pathways when producing rAAVs. The required expression balance emphasizes the critical need to fine-tune the concentration of all these different elements. The use of design of experiments (DOE) to find optimal ratios is a powerful method to streamline the process. However, the choice of the DOE method and design construction is crucial to avoid misleading results. In this work, we examined and compared four distinct DOE approaches: rotatable central composite design (RCCD), Box-Behnken design (BBD), face-centered central composite design (FCCD), and mixture design (MD). We compared the abilities of the different models to predict optimal ratios and interactions among the plasmids and the transfection reagent. Our findings revealed that blocking is essential to reduce the variability caused by uncontrolled random effects and that MD coupled with FCCD outperformed all other approaches, improving volumetric productivity 109-fold. These outcomes underscore the importance of selecting a model that can effectively account for the biological context, ultimately yielding superior results in optimizing rAAV production.
Keywords: AAV; Box-Behnken; DOE; biomanufacturing; design of experiments; gene therapy; mixture design; optimization; recombinant adeno-associated virus; response surface methodology.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Enhancing the production of adeno-associated virus (AAV)2 and AAV9 with high full capsid ratio in HEK293 cells through design-of-experiment optimization of triple plasmid ratio.Biotechnol J. 2024 Mar;19(3):e2300667. doi: 10.1002/biot.202300667. Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 38479987
-
Molecular design for recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vector production.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Feb;102(3):1045-1054. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8670-1. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29204900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical challenges and advances in recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) biomanufacturing.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2023 Sep;120(9):2601-2621. doi: 10.1002/bit.28412. Epub 2023 May 1. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2023. PMID: 37126355 Review.
-
Creation of a High-Yield AAV Vector Production Platform in Suspension Cells Using a Design-of-Experiment Approach.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020 Jun 3;18:312-320. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2020.06.004. eCollection 2020 Sep 11. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020. PMID: 32671134 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome profiling and vector yield optimization in a recombinant adeno-associated virus-producing yeast model.Microbiologyopen. 2020 Dec;9(12):e1136. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1136. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Microbiologyopen. 2020. PMID: 33166081 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Improved productivity of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) via triple transfection of HEK293 cells using perfusion cultivation.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2025 Jul;48(7):1159-1169. doi: 10.1007/s00449-025-03167-9. Epub 2025 Apr 26. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2025. PMID: 40285883
-
Adaptive Machine Learning Framework enables Unprecedented Yield and Purity of Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors for Gene Therapy.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 24:2025.05.23.655859. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.23.655859. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40475650 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Mixture design as a tool for improving full-to-empty particle ratios across various GOIs in rAAV production.Gene Ther. 2025 Jun 20. doi: 10.1038/s41434-025-00546-5. Online ahead of print. Gene Ther. 2025. PMID: 40542086
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

