Risk factors for regional lymph node metastasis in rectal neuroendocrine tumors: a population-based study
- PMID: 39296902
- PMCID: PMC11408165
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1383047
Risk factors for regional lymph node metastasis in rectal neuroendocrine tumors: a population-based study
Abstract
Introduction: The identification of risk factors for regional lymph node (r-LN) metastasis in rectal neuroendocrine tumors (R-NETs) remains challenging. Our objective was to investigate the risk factors associated with patients diagnosed with R-NETs exhibiting r-LN metastasis.
Methods: Patient information was obtained from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database, complemented by data from the West China Hospital (WCH) databases. The construction cohort comprised patients diagnosed with R-NETs from the SEER database, while cases from the WCH database were utilized as the validation cohort. A novel nomogram was developed to predict the probability of r-LN metastasis, employing a logistic regression model.
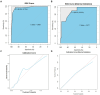
Results: Univariate analysis identified four independent risk factors associated with poor r-LN metastasis: age (HR = 1.027, p < 0.05), grade (HR = 0.010, p < 0.05), T stage (HR = 0.010, p < 0.05), and tumor size (HR = 0.005, p < 0.05). These factors were selected as predictors for nomogram construction.
Discussion: The novel nomogram serves as a reliable tool for predicting the risk of r-LN metastasis, providing clinicians with valuable assistance in identifying high-risk patients and tailoring individualized treatments.
Keywords: SEER; West China hospital databases; rectal neuroendocrine tumors; regional lymph node metastasis; tumor size.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Li, Wang, Chang, Lv, Li and Cao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

