Versatile whey acidic protein four-disulfide core domain proteins: biology and role in diseases
- PMID: 39296934
- PMCID: PMC11408880
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1459129
Versatile whey acidic protein four-disulfide core domain proteins: biology and role in diseases
Abstract
The Whey acidic protein four-disulfide core (WFDC) protein family consists of proteins with one or more WFDC domains which are ubiquitously expressed throughout the body of human and perform a wide range of functions, including antiprotease, antibacterial, and immunomodulatory functions. Aberrant expression of WFDC proteins is associated with human diseases. However, review on the WFDC protein family is limited and insufficient. Furthermore, a systematic summary of the underlying mechanisms of WFDC protein activity is lacking. In this review, we give a summary of the structural basis and molecular function of these proteins and review the immune regulatory mechanisms and signaling pathways of WFDC proteins in the development of certain diseases. Furthermore, we discuss the diagnostic and prognostic potential of multiple WFDC proteins in the aforementioned conditions, as well as their prospective use. At last, we also discuss the progress of WFDC protein in clinical trials and put forward some research difficulties and the directions of follow-up research. Our review highlights the functional diversity and clinical significance of WFDC proteins family, while providing potential targets for drug development and innovative therapeutic strategies, this review lays the foundation and direction for future research on WFDC proteins.
Keywords: WFDC proteins; biomarker; cancer; heart failure; inflammatory disease; signaling/signaling pathways.
Copyright © 2024 Wen, Jiang, Wang and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

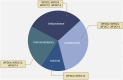
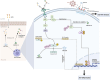

References
-
- Asher M. I., Montefort S., Björkstén B., Lai C. K. W., Strachan D. P., Weiland S. K., et al. (2006). Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet. 368 (9537), 733–743. 10.1016/s0140-6736(06)69283-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

