Causal effects of obstructive sleep apnea on chronic kidney disease and renal function: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 39296957
- PMCID: PMC11408330
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1323928
Causal effects of obstructive sleep apnea on chronic kidney disease and renal function: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Background: Observational studies have suggested an association between obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), chronic kidney disease (CKD), and renal function, and vice versa. However, the results from these studies are inconsistent. It remains unclear whether there are causal relationships and in which direction they might exist.
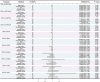
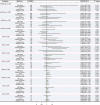
Methods: We used a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) method to investigate the bidirectional causal relation between OSA and 7 renal function phenotypes [creatinine-based estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFRcrea), cystatin C-based estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFRcys), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), rapid progress to CKD, rapid decline of eGFR, urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR) and CKD]. The genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary statistics of OSA were retrieved from FinnGen Consortium. The CKDGen consortium and UK Biobank provided GWAS summary data for renal function phenotypes. Participants in the GWAS were predominantly of European ancestry. Five MR methods, including inverse variance weighted (IVW), MR-Egger, simple mode, weighted median, and weighted mode were used to investigate the causal relationship. The IVW result was considered the primary outcome. Then, Cochran's Q test and MR-Egger were used to detect heterogeneity and pleiotropy. The leave-one-out analysis was used for testing the stability of MR results. RadialMR was used to identify outliers. Bonferroni correction was applied to test the strength of the causal relationships (p < 3.571 × 10-3).
Results: We failed to find any significant causal effect of OSA on renal function phenotypes. Conversely, when we examined the effects of renal function phenotypes on OSA, after removing outliers, we found a significant association between BUN and OSA using IVW method (OR: 2.079, 95% CI: 1.516-2.853; p = 5.72 × 10-6).
Conclusion: This MR study found no causal effect of OSA on renal function in Europeans. However, genetically predicted increased BUN is associated with OSA development. These findings indicate that the relationship between OSA and renal function remains elusive and requires further investigation.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; causal relationship; chronic kidney disease; obstructive sleep apnea; renal function.
Copyright © 2024 Hou, Li, Xiao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

