Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: audiological profile during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 39296959
- PMCID: PMC11408228
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1415068
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: audiological profile during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
Introduction: Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) is an otological emergency that requires prompt recognition and intervention to prevent devastating impacts on people's lives. During the COVID-19 pandemic, sensory deprivations have been reported in patients positive for SARS-CoV-2 virus, including deleterious effects on the auditory pathway. This study aims to describe the audiological profile of individuals with SSNHL during the COVID-19 pandemic and to correlate hearing recovery in subgroups of individuals with or without COVID-19.
Methods: Prospective cohort including patients diagnosed with SSNHL evaluated in a tertiary care center between March 2020 and September 2022. Hearing loss was confirmed with pure-tone and speech audiometry, with Speech Recognition Threshold (SRT) and word recognition score (WRS). Audiometric testing was performed at the moment of diagnosis, then 7, 30 and 120 days after diagnosis. The average degree of hearing loss was assessed by calculating the 4-frequency pure tone average (4fPTA). The investigation of COVID-19 included RT-PCR technique for the SARS-CoV-2 virus and collection of information regarding disease severity. A statistical analysis was performed using an analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) model to compare the 4fPTA between the four groups (with and without a history of COVID-19, unilateral and bilateral cases) at the end of the follow-up period.
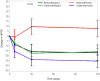
Results: Fifty-two patients with SSNHL were assessed, 40 (76.9%) with unilateral and 12 (23.1%) with bilateral hearing loss, totaling 64 ears included. Of those, 15 (28.8%) patients tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 and were symptomatic for COVID-19. Of all unilateral cases, 22.5% were seropositive and showed symptoms of COVID-19, a number that increased to 50% for bilateral cases. Comparing the COVID-19 positive groups, individuals with unilateral SSNHL went from 40 dB as their average 4fPTA at onset to 20 dB as their average 4fPTA after 120 days, whereas those with bilateral SSNHL went from an initial average of 60 dB to a final average of 66 dB. Although the 4fPTA value of individuals with unilateral SSNHL improved in 7 days, the mean values showed no significant difference between positive and negative groups. There was a higher incidence of bilateral simultaneous SSNHL in patients who had not been vaccinated against COVID-19 and who presented with symptoms of severe COVID-19.
Conclusion: Infection with SARS-CoV-2 resulted in more severe SSNHL, in bilateral SSNHL, and in poorer recovery from SSNHL in bilateral cases. Bilateral SSNHL was seen more frequently in patients who had not received vaccination against COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; audiological profile; audiology; neurotology; sudden deafness; sudden sensorineural hearing loss.
Copyright © 2024 Peron, Scott, Soeiro, do Amaral, Chandrasekhar and de Oliveira Penido.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- De KA. Sudden complete or partial loss of function of the octavus-system in apparently normal persons. Acta Otolaryngol. (1944) 32:407–29. doi: 10.3109/00016484409119921 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous