Endothelial TGF-β Signaling Regulates Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition During Arteriovenous Fistula Remodeling in Mice With Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 39297205
- PMCID: PMC11593991
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.320933
Endothelial TGF-β Signaling Regulates Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition During Arteriovenous Fistula Remodeling in Mice With Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
Background: Arteriovenous fistulae (AVF) are the preferred vascular access for hemodialysis in patients with end-stage kidney disease. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is associated with endothelial injury, impaired AVF maturation, and reduced patency, as well as utilization. Because CKD is characterized by multiple pathophysiological processes that induce endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT), we hypothesized that CKD promotes EndMT during venous remodeling and that disruption of endothelial TGF (transforming growth factor)-β signaling inhibits EndMT to prevent AVF failure even in the end-stage kidney disease environment.
Methods: The mouse 5/6 nephrectomy and aortocaval fistula models were used. CKD was created via 5/6 nephrectomy, with controls of no (0/6) or partial (3/6) nephrectomy in C57BL/6J mice. AVF were created in mice with knockdown of TGF-βR1/R2 (TGF-β receptors type 1/2) in either smooth muscle cells or endothelial cells. AVF diameters and patency were measured and confirmed by serial ultrasound examination. AVF, both murine and human, were examined using Western blot, histology, and immunofluorescence. Human and mouse endothelial cells were used for in vitro experiments.
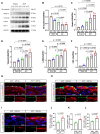
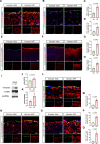
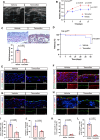
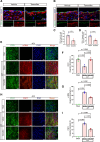
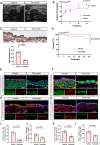
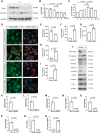
Results: CKD accelerates TGF-β activation and promotes EndMT that is associated with increased AVF wall thickness and reduced patency in mice. Inhibition of TGF-β signaling in both endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells decreased smooth muscle cell proliferation in the AVF wall, attenuated EndMT, and was associated with reduced wall thickness, increased outward remodeling, and improved AVF patency. Human AVF also showed increased TGF-β signaling and EndMT.
Conclusions: CKD promotes EndMT and reduces AVF patency. Inhibition of TGF-β signaling, especially disruption of endothelial cell-specific TGF-β signaling, attenuates EndMT and improves AVF patency in mouse AVF. Inhibition of EndMT may be a therapeutic approach of translational significance to improve AVF patency in human patients with CKD.
Keywords: TGF-β; arteriovenous fistula; cell differentiation; endothelial cells; endothelial-mesenchymal transition; kidney failure, chronic; myocytes, smooth muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Comment in
-
TGF-β: A Wrench in the Gears of Arteriovenous Fistula Maturation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024 Dec;44(12):2527-2529. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.321827. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024. PMID: 39445425 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, Li Z, Naicker S, Plattner B, Saran R, Wang AY, Yang CW. Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet. 2013;382:260–272. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60687-X - PubMed
-
- Naghavi M, Wang HD, Lozano R, Davis A, Liang XF, Zhou MG, Vollset SE, Ozgoren AA, Abdalla S, Abd-Allah F, et al. . Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;385:117–171. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(14)61682-2 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Almasri J, Alsawas M, Mainou M, Mustafa RA, Wang Z, Woo K, Cull DL, Murad MH. Outcomes of vascular access for hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Vasc Surg. 2016;64:236–243. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2016.01.053 - PubMed
-
- Murad MH, Elamin MB, Sidawy AN, Malaga G, Rizvi AZ, Flynn DN, Casey ET, McCausland FR, McGrath MM, Vo DH, et al. . Autogenous versus prosthetic vascular access for hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Vasc Surg. 2008;48:34S–47S. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2008.08.044 - PubMed
-
- Langer S, Kokozidou M, Heiss C, Kranz J, Kessler T, Paulus N, Kruger T, Jacobs MJ, Lente C, Koeppel TA. Chronic kidney disease aggravates arteriovenous fistula damage in rats. Kidney Int. 2010;78:1312–1321. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.353 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

