Urinary Metal Levels and Coronary Artery Calcification: Longitudinal Evidence in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 39297845
- PMCID: PMC11804863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2024.07.020
Urinary Metal Levels and Coronary Artery Calcification: Longitudinal Evidence in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
Abstract
Background: Exposure to metals, a newly recognized risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD), could be related to atherosclerosis progression.
Objectives: The authors hypothesized that higher urinary levels of nonessential (cadmium, tungsten, uranium) and essential (cobalt, copper, zinc) metals previously associated with CVD would be associated with baseline and rate of change of coronary artery calcium (CAC) progression, a subclinical marker of CVD in MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis).
Methods: We analyzed data from 6,418 MESA participants with spot urinary metal levels at baseline (2000-2002) and 1 to 4 repeated, continuous measures of CAC over a 10-year period. We used linear mixed-effect models to assess the association of baseline urinary metal levels with baseline CAC and cumulative change in CAC over a 10-year period. Urinary metals (μg/g creatinine) and CAC were log transformed. Models were adjusted for baseline sociodemographic factors, estimated glomerular filtration rate, lifestyle factors, and clinical factors.
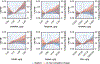
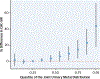
Results: At baseline, the median CAC was 6.3 (Q1-Q3: 0.7-58.2). Comparing the highest to lowest quartile of urinary cadmium, CAC levels were 51% (95% CI: 32%, 74%) higher at baseline and 75% (95% CI: 47%, 107%) higher over the 10-year period. For urinary tungsten, uranium, and cobalt, the corresponding CAC levels over the 10-year period were 45% (95% CI: 23%, 71%), 39% (95% CI: 17%, 64%), and 47% (95% CI: 25%, 74%) higher, respectively, with no difference for models with and without adjustment for clinical factors. For copper and zinc, the corresponding estimates dropped from 55% to 33% and from 85% to 57%, respectively, after adjustment for clinical factors. The associations of metals with CAC were comparable in magnitude to those for classical CVD risk factors.
Conclusions: Exposure to metals was generally associated with extent of coronary calcification at baseline and follow-up. These findings support that metals are associated with the progression of atherosclerosis, potentially providing a novel strategy for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis progression.
Keywords: cadmium; cardiovascular disease; cobalt; copper; coronary artery calcification; longitudinal; metals; mixed models; prospective; tungsten; uranium; zinc.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding Support and Author Disclosures The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) is supported by contracts 75N92020D00001, HHSN268201500003I, N01-HC-95159, 75N92020D00005, N01-HC-95160, 75N92020D00002, N01-HC-95161, 75N92020D00003, N01-HC-95162, 75N92020D00006, N01-HC-95163, 75N92020D00004, N01-HC-95164, 75N92020D00007, N01-HC-95165, N01-HC-95166, N01-HC-95167, N01-HC-95168, and N01-HC-95169 from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and by grants UL1-TR-000040, UL1-TR-001079, and UL1-TR-001420 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS). This publication was developed under the Science to Achieve Results (STAR) research assistance agreements, No. RD831697 (MESA Air) and RD-83830001 (MESA Air Next Stage), awarded by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). It has not been formally reviewed by the EPA. The views expressed in this document are solely those of the authors and the EPA does not endorse any products or commercial services mentioned in this publication. Work in the authors’ laboratories is also supported in part by NIH grants P42ES023716, P42ES010349, P42ES033719, P30ES009089, T32ES007322, R01ES029967, R01HL155576, R01ES029967, and R01ES028758. The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures


Update of
-
Urinary Metal Levels and Coronary Artery Calcification: Longitudinal Evidence in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA).medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 1:2023.10.31.23297878. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.31.23297878. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Am Coll Cardiol. 2024 Oct 15;84(16):1545-1557. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2024.07.020. PMID: 37961623 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Rajagopalan S, Landrigan PJ. Pollution and the heart. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:1881–1892. - PubMed
-
- Grau-Perez M, Caballero-Mateos MJ, Domingo-Relloso A, et al. Toxic metals and subclinical atherosclerosis in carotid, femoral, and coronary vascular territories: the Aragon Workers Health Study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2022;42:87–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES028758/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES010349/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES033719/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES023716/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR001874/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES007322/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL155576/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES029967/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES009089/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

