Clinical bioinformatics desiderata for molecular tumor boards
- PMID: 39297878
- PMCID: PMC11411775
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbae447
Clinical bioinformatics desiderata for molecular tumor boards
Abstract
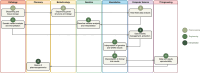
Clinical Bioinformatics is a knowledge framework required to interpret data of medical interest via computational methods. This area became of dramatic importance in precision oncology, fueled by cancer genomic profiling: most definitions of Molecular Tumor Boards require the presence of bioinformaticians. However, all available literature remained rather vague on what are the specific needs in terms of digital tools and expertise to tackle and interpret genomics data to assign novel targeted or biomarker-driven targeted therapies to cancer patients. To fill this gap, in this article, we present a catalog of software families and human skills required for the tumor board bioinformatician, with specific examples of real-world applications associated with each element presented.
Keywords: biobanking; clinical bioinformatics; clinical informatics; data engineering; decision support tools; molecular tumor board; molecular tumor registry; variant actionability; variant annotation.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

References
-
- Tsimberidou AM, Kahle M, Vo HH. et al. . Molecular tumour boards—Current and future considerations for precision oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2023;20:843–63. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41571-023-00824-4. - PubMed
-
- Tamborero D, Dienstmann R, Rachid MH. et al. . The molecular tumor board portal supports clinical decisions and automated reporting for precision oncology. Nature Cancer 2022;3:251–61. https://www.nature.com/articles/s43018-022-00332-x. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

