Inhibition of hTERT/telomerase/telomere mediates therapeutic efficacy of osimertinib in EGFR mutant lung cancer
- PMID: 39297884
- PMCID: PMC11413468
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20240435
Inhibition of hTERT/telomerase/telomere mediates therapeutic efficacy of osimertinib in EGFR mutant lung cancer
Abstract
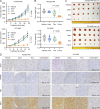
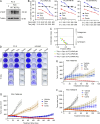
The inevitable acquired resistance to osimertinib (AZD9291), an FDA-approved third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) for the treatment of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring EGFR activating or T790M resistant mutations, limits its long-term clinical benefit. Telomere maintenance via telomerase reactivation is linked to uncontrolled cell growth and is a cancer hallmark and an attractive cancer therapeutic target. Our effort toward understanding the action mechanisms, including resistance mechanisms, of osimertinib has led to the identification of a novel and critical role in maintaining c-Myc-dependent downregulation of hTERT, a catalytic subunit of telomerase, and subsequent inhibition of telomerase/telomere and induction of telomere dysfunction in mediating therapeutic efficacy of osimertinib. Consequently, osimertinib combined with the telomere inhibitor, 6-Thio-dG, which is currently tested in a phase II trial, effectively inhibited the growth of osimertinib-resistant tumors, regressed EGFRm NSCLC patient-derived xenografts, and delayed the emergence of acquired resistance to osimertinib, warranting clinical validation of this strategy to manage osimertinib acquired resistance.
© 2024 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: T. Leal reported personal fees from AstraZeneca, Daiichi-Sankio, Janssen, Takeda, EMD Serono, Eisai, Novocure, Amgen, Roche/Genentech, Regeneron, Jazz, Catalyst, OncoC4, Pfizer, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, AbbVie, Gilead, Black Diamond, and Boehringer-Ingelheim outside the submitted work. S.S. Ramalingam reported grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Merck, Pfizer, and Amgen outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures










References
-
- Aras, G., Kanmaz D., Urer N., Purisa S., Kadakal F., Yentürk E., and Tuncay E.. 2013. Immunohistochemical expression of telomerase in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: Prediction of metastasis and prognostic significance. Anticancer Res. 33:2643–2650. - PubMed
-
- Camps, C., Sirera R., Bremnes R.M., Ródenas V., Blasco A., Safont M.J., Garde J., Juarez A., Caballero C., Sanchez J.J., et al. . 2006. Quantification in the serum of the catalytic fraction of reverse telomerase: A useful prognostic factor in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 26:4905–4909. - PubMed
-
- Chen, Z., Vallega K.A., Chen H., Zhou J., Ramalingam S.S., and Sun S.Y.. 2022. The natural product berberine synergizes with osimertinib preferentially against MET-amplified osimertinib-resistant lung cancer via direct MET inhibition. Pharmacol. Res. 175:105998. 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105998 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

