Acute cardiovascular responses to the 100-mi Western States Endurance Run
- PMID: 39298619
- PMCID: PMC11563584
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00412.2024
Acute cardiovascular responses to the 100-mi Western States Endurance Run
Abstract
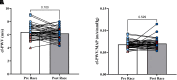
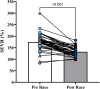
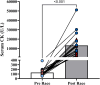
Ultramarathon participation is growing in popularity and exposes runners to unique stressors including extreme temperatures, high altitude, and exceedingly long exercise duration. However, the acute effects of ultramarathon participation on the cardiovascular system are not well understood. To determine the acute effects of trail ultramarathon participation on central artery stiffness and hemodynamics, 41 participants (9 F, 32 M) participating in the 2023 Western States Endurance Run underwent measures of carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cf-PWV) and pulse wave analysis pre- and <1 h post-race. Subendocardial viability ratio (SEVR) was calculated from central blood pressure (BP) waveforms. Serum was analyzed for creatine kinase (CK) activity as a measure of muscle damage. Normally distributed data are presented as means ± standard deviation (SD), and nonnormally distributed data are presented as median (interquartile range). Runners were middle-aged and generally lean [age = 44 ± 9 yr, body mass index (BMI) = 22.7 ± 1.8 kg·m-2]. There was no difference in cf-PWV from pre- to post-race (pre = 6.4 ± 1.0, post = 6.2 ± 0.85 m/s, P = 0.104), a finding that persisted after adjusting for mean arterial pressure (P = 0.563). Systolic and diastolic BPs were lower post-race (pre = 129/77 ± 9/7, post = 122/74 ± 10/8 mmHg, P < 0.001). Augmentation index (AIx; pre = 17.3 ± 12.2, post = 6.0 ± 13.7%, P < 0.001), AIx normalized to a heart rate of 75 beats/min (P = 0.043), reflection magnitude (pre = 55.5(49.0-60.8), post = 45.5(41.8-48.8)%, P < 0.001), and SEVR (pre = 173.0(158.0-190.0), post = 127.5(116.5-145.8)%, P < 0.001) were reduced post-race. CK increased markedly from pre- to post-race (pre = 111(85-162), post = 11,973(5,049-17,954) U/L, P < 0.001). Completing a 161-km trail ultramarathon does not affect central arterial stiffness and acutely reduces BP despite eliciting profound muscle damage. However, the reduced post-race SEVR suggests a short-term mismatch between myocardial work and coronary artery perfusion.NEW AND NOTEWORTHY Ultramarathon participation is growing dramatically. However, the acute cardiovascular effects of completing a 161-km trail ultramarathon remain unknown. We examined the acute effects of completing the 2023 Western States Endurance Run on arterial stiffness and central hemodynamics in a relatively large sample of males and females. We observed dramatic postexercise hypotension, reductions in reflected wave amplitude and reduced subendocardial viability ratio post-race. These findings suggest that ultramarathon participation has few negative effects on cardiovascular health.
Keywords: arterial stiffness; central hemodynamics; exercise physiology; pulse wave analysis; ultramarathon.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Austin Robinson is an editor of
Figures
References
-
- Lear SA, Hu W, Rangarajan S, Gasevic D, Leong D, Iqbal R, Casanova A, Swaminathan S, Anjana RM, Kumar R, Rosengren A, Wei L, Yang W, Chuangshi W, Huaxing L, Nair S, Diaz R, Swidon H, Gupta R, Mohammadifard N, Lopez-Jaramillo P, Oguz A, Zatonska K, Seron P, Avezum A, Poirier P, Teo K, Yusuf S. The effect of physical activity on mortality and cardiovascular disease in 130 000 people from 17 high-income, middle-income, and low-income countries: the PURE study. Lancet 390: 2643–2654, 2017. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31634-3. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR003096/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL147998/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AG062319/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR003096/HHS | NIH | National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS)
- K01HL147998/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- U54AG062319/HHS | NIH | National Institute on Aging (NIA)
- L30 HL154374/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01HL160772/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- 23CDA1037938/American Heart Association (AHA)
- R15 HL165325/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL160772/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R15HL165325/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- K01HL164978/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- K01 HL164978/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Western States Endurance Run Medical Research Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

