Electron transfer in the respiratory chain at low salinity
- PMID: 39300056
- PMCID: PMC11413003
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52475-3
Electron transfer in the respiratory chain at low salinity
Abstract
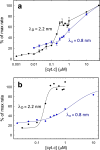
Recent studies have established that cellular electrostatic interactions are more influential than assumed previously. Here, we use cryo-EM and perform steady-state kinetic studies to investigate electrostatic interactions between cytochrome (cyt.) c and the complex (C) III2-IV supercomplex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae at low salinity. The kinetic studies show a sharp transition with a Hill coefficient ≥2, which together with the cryo-EM data at 2.4 Å resolution indicate multiple cyt. c molecules bound along the supercomplex surface. Negatively charged loops of CIII2 subunits Qcr6 and Qcr9 become structured to interact with cyt. c. In addition, the higher resolution allows us to identify water molecules in proton pathways of CIV and, to the best of our knowledge, previously unresolved cardiolipin molecules. In conclusion, the lowered electrostatic screening renders engagement of multiple cyt. c molecules that are directed by electrostatically structured CIII2 loops to conduct electron transfer between CIII2 and CIV.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

