PIP2 inhibits pore opening of the cyclic nucleotide-gated channel SthK
- PMID: 39300080
- PMCID: PMC11413322
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52469-1
PIP2 inhibits pore opening of the cyclic nucleotide-gated channel SthK
Abstract
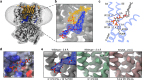
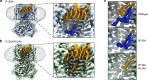
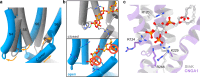
The signaling lipid phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) regulates many ion channels. It inhibits eukaryotic cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channels while activating their relatives, the hyperpolarization-activated and cyclic nucleotide-modulated (HCN) channels. The prokaryotic SthK channel from Spirochaeta thermophila shares features with CNG and HCN channels and is an established model for this channel family. Here, we show SthK activity is inhibited by PIP2. A cryo-EM structure of SthK in nanodiscs reveals a PIP2-fitting density coordinated by arginine and lysine residues from the S4 helix and the C-linker, located between voltage-sensing and pore domains of adjacent subunits. Mutation of two arginine residues weakens PIP2 inhibition with the double mutant displaying insensitivity to PIP2. We propose that PIP2 inhibits SthK by gluing S4 and S6 together, stabilizing a resting channel conformation. The PIP2 binding site is partially conserved in CNG channels suggesting the possibility of a similar inhibition mechanism in the eukaryotic homologs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Fernandis, A. Z. & Wenk, M. R. Membrane lipids as signaling molecules. Curr. Opin. Lipidol.18, 121 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Manna, M., Nieminen, T. & Vattulainen, I. Understanding the role of lipids in signaling through atomistic and multiscale simulations of cell membranes. Annu. Rev. Biophysics48, 421–439 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

