Predictive modeling of hepatitis B viral dynamics: a caputo derivative-based approach using artificial neural networks
- PMID: 39300092
- PMCID: PMC11413037
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-70788-7
Predictive modeling of hepatitis B viral dynamics: a caputo derivative-based approach using artificial neural networks
Abstract
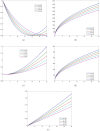
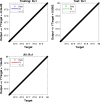
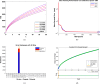
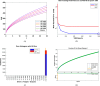
A fractional model for the kinetics of hepatitis B transmission was developed. The hepatitis B virus significantly affects the world's economic and health systems. Acute and chronic carrier phases play a crucial part in the spread of the HBV infection. The Hepatitis B infection can be spread by chronic carriers even though they show no symptoms. In this article, we looked into the Hepatitis B virus's various stages of infection-related transmission and built a nonlinear epidemic. Then, a fractional hepatitis B virus model using a Caputo derivative and vaccine effects is created. First, we determined the proposed model's essential reproductive value and equilibria. With the aid of Fixed Point Theory, a qualitative analysis of the problem's approximative root has been produced. The Adams-Bashforth predictor-corrector scheme is used to aid in the iterative approximate technique's evaluation of the fractional system under consideration that has the Caputo derivative. In the final section, a graphical representation compares various noninteger orders and displays the discovered scheme findings. In this study, we've utilized Artificial Neural Network (ANN) techniques to partition the dataset into three categories: training, testing, and validation. Our analysis delves deep into each category, comprehensively examining the dataset's characteristics and behaviors within these divisions. The study comprehensively analyzes the fractional HBV transmission model, incorporating both mathematical and computational approaches. The findings contribute to a better understanding of the dynamics of HBV infection and can inform the development of effective public health interventions.
Keywords: Adams-Bashforth; Artificial neural networking; Fractional derivative; Mild solution; Mittag-Leffler; Numerical simulations; Vaccination.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Nowak, M. & May, R. M. Virus Dynamics: Mathematical Principles of Immunology and Virology: Mathematical Principles of Immunology and Virology (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2000).
-
- Din, A., Li, Y. & Yusuf, A. Delayed hepatitis B epidemic model with stochastic analysis. Chaos Solitons Fractals146, 110839 (2021). - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

