Is ibrutinib-related atrial fibrillation dose dependent? Insights from an individual case level analysis of the World Health Organization pharmacovigilance database
- PMID: 39300222
- PMCID: PMC11588646
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-024-02413-5
Is ibrutinib-related atrial fibrillation dose dependent? Insights from an individual case level analysis of the World Health Organization pharmacovigilance database
Abstract
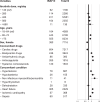
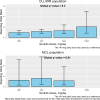
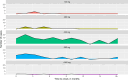
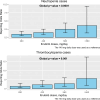
Whether ibrutinib-related atrial fibrillation (IRAF) is a dose-dependent adverse drug reaction (ADR) and whether ibrutinib should be discontinued or dose-reduced in case of IRAF occurrence remains unknown. Using the World Health Organization individual case safety report pharmacovigilance database, VigiBase®, we aimed to determine the association between ibrutinib dosing regimens and IRAF reporting. Ibrutinib daily dose was extracted from IRAF cases from VigiBase® and was divided into 5 ibrutinib dosing regimen (140-280-420-560 and >560 mg/day). Disproportionality analysis was used to evaluate the association between IRAF reporting and ibrutinib daily dose, through logistic regression. Single term deletions produced the ibrutinib daily dose global p-value. Then, a multivariable adjusted reporting odds-ratio with its 95% confidence interval was calculated for each ibrutinib dosing regimen, against the lowest dosing regimen (140 mg/day) as reference. A total of 1162 IRAF cases were identified in VigiBase® (n = 62 for ibrutinib 140 mg/day, 114 for ibrutinib 280 mg/day, 811 for ibrutinib 420 mg/day, 164 for ibrutinib 560 mg/day and 11 for ibrutinib >560 mg/day). After adjustment on several variables of interest, IRAF reporting was not significantly associated with ibrutinib dosing regimen (p = 0.09). Our results from Vigibase® do not support IRAF as a dose-dependent ADR (ClinicalTrial registration number: NCT06224452).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JA reports honoraria for presentations and consulting fees from Biotronik, Bioserenity, Amgen, BMS, Pfizer, Boerhinger, Bayer, Astra Zeneca, Janssen, Servier, and Novartis, outside of the submitted work. DL reports honoraria for presentations and consulting fees from Astrazeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, Pfizer and Takeda, outside of the submitted work. CD reports honoraria for presentations and consulting fees from Bioserenity and Pfizer, outside of the submitted work. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, Caligaris-Cappio F, Dighiero G, Döhner H, et al. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood. 2018;131:2745–60. - PubMed
-
- Leong DP, Caron F, Hillis C, Duan A, Healey JS, Fraser G, et al. The risk of atrial fibrillation with ibrutinib use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood. 2016;128:138–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

