The splicing factor hnRNPL demonstrates conserved myocardial regulation across species and is altered in heart failure
- PMID: 39300280
- PMCID: PMC11560511
- DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.15020
The splicing factor hnRNPL demonstrates conserved myocardial regulation across species and is altered in heart failure
Abstract
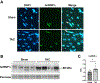
Heart failure (HF) is highly prevalent. Mechanisms underlying HF remain incompletely understood. Splicing factors (SF), which control pre-mRNA alternative splicing, regulate cardiac structure and function. This study investigated regulation of the splicing factor heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein-L (hnRNPL) in the failing heart. hnRNPL protein increased in left ventricular tissue from mice with transaortic constriction-induced HF and from HF patients. In left ventricular tissue, hnRNPL was detected predominantly in nuclei. Knockdown of the hnRNPL homolog Smooth in Drosophila induced cardiomyopathy. Computational analysis of predicted mouse and human hnRNPL binding sites suggested hnRNPL-mediated alternative splicing of tropomyosin, which was confirmed in C2C12 myoblasts. These findings identify hnRNPL as a sensor of cardiac dysfunction and suggest that disturbances of hnRNPL affect alternative splicing in HF.
Keywords: cardiomyopathy; heart failure; hnRNPL; mRNA splicing; splicing factors.
© 2024 Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST & ETHICS STATEMENT
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. May 3 2022;79(17):1757–1780. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.12.011 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

