Randomized phase 2 study of valproic acid combined with simvastatin and gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel-based regimens in untreated metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients: the VESPA trial study protocol
- PMID: 39300376
- PMCID: PMC11414294
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12936-w
Randomized phase 2 study of valproic acid combined with simvastatin and gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel-based regimens in untreated metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients: the VESPA trial study protocol
Abstract
Background: Metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (mPDAC) patients have very poor prognosis highlighting the urgent need of novel treatments. In this regard, repurposing non-oncology already-approved drugs might be an attractive strategy to offer more-effective treatment easily tested in clinical trials. Accumulating evidence suggests that epigenetic deregulation is a hallmark of cancer contributing to treatment resistance in several solid tumors, including PDAC. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) are epigenetic drugs we have investigated preclinically and clinically as anticancer agents. Valproic acid (VPA) is a generic low-cost anticonvulsant and mood stabilizer with HDAC inhibitory activity, and anticancer properties also demonstrated in PDAC models. Statins use was reported to be associated with lower mortality risk in patients with pancreatic cancer and statins have been shown to have a direct antitumor effect when used alone or in combination therapy. We recently showed capability of VPA/Simvastatin (SIM) combination to potentiate the antitumor activity of gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel in vitro and in vivo PDAC preclinical models.
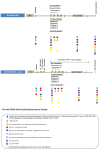
Methods/design: VESPA is a patient-centric open label randomized multicenter phase-II investigator-initiated trial, evaluating the feasibility, safety, and efficacy of VPA/SIM plus first line gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel-based regimens (AG or PAXG) (experimental arm) versus chemotherapy alone (standard arm) in mPDAC patients. The study involves Italian and Spanish oncology centers and includes an initial 6-patients safety run-in-phase. A sample size of 240 patients (120 for each arm) was calculated under the hypothesis that the addition of VPA/SIM to gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel-based regimens may extend progression free survival from 6 to 9 months in the experimental arm. Secondary endpoints are overall survival, response rate, disease control rate, duration of response, CA 19.9 reduction, toxicity, and quality of life. The study includes a patient engagement plan and complementary biomarkers studies on tumor and blood samples.
Conclusions: VESPA is the first trial evaluating efficacy and safety of two repurposed drugs in oncology such as VPA and SIM, in combination with standard chemotherapy, with the aim of improving mPDAC survival. The study is ongoing. Enrollment started in June 2023 and a total of 63 patients have been enrolled as of June 2024.
Trial registration: EudraCT number: 2022-004154-63; ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT05821556, posted 2023/04/20.
Keywords: Drug repurposing; Gemcitabine, nab-paclitaxel; Pancreatic cancer; Simvastatin; Valproic acid.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/13-Pancreas-fact-sheet.pdf, S. International Agency for Research in Cancer- World Health Organization Pancreatic Cancer Fact Sheet. 2020.
-
- Hutchinson L, Kirk R. High drug attrition rates–where are we going wrong? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;8(4):189–90. - PubMed
-
- Lambert A, Conroy T, Ducreux M. Future directions in drug development in pancreatic cancer. Semin Oncol. 2021;48(1):47–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

