Macrophage membrane-camouflaged biomimetic nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis treatment via modulating macrophage polarization
- PMID: 39300463
- PMCID: PMC11414146
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02822-9
Macrophage membrane-camouflaged biomimetic nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis treatment via modulating macrophage polarization
Abstract
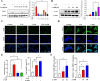
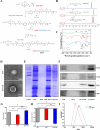
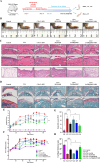
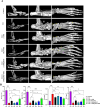
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a debilitating autoimmune disease characterized by chronic joint inflammation and cartilage damage. Current therapeutic strategies often result in side effects, necessitating the development of targeted and safer treatment options. This study introduces a novel nanotherapeutic system, 2-APB@DGP-MM, which utilizes macrophage membrane (MM)-encapsulated nanoparticles (NPs) for the targeted delivery of 2-Aminoethyl diphenylborinate (2-APB) to inflamed joints more effectively. The NPs are designed with a matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-cleavable peptide, allowing for MMP-responsive drug release within RA microenvironment. Comprehensive in vitro and in vivo assays confirmed the successful synthesis and loading of 2-APB into the DSPE-GPLGVRGC-PEG (DGP) NPs, as well as their ability to repolarize macrophages from a pro-inflammatory M1 to an anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype. The NPs demonstrated high biocompatibility, low cytotoxicity, and enhanced cellular uptake. In a collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model, intra-articular injection of 2-APB@DGP-MM significantly reduced synovial inflammation and cartilage destruction. Histological analysis corroborated these findings, demonstrating marked improvements in joint structure and delayed disease progression. Above all, the 2-APB@DGP-MM nanotherapeutic system offers a promising and safe approach for RA treatment by modulating macrophage polarization and delivering effective agents to inflamed joints.
Keywords: 2-APB; Inflammation; Macrophage polarization; Membrane-encapsulated nanoparticles; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2016;388:2023–38. - PubMed
-
- Fan Z, Li J, Liu J, Jiao H, Liu B. Anti-inflammation and joint lubrication dual effects of a novel hyaluronic acid/curcumin nanomicelle improve the efficacy of rheumatoid arthritis therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:23595–604. - PubMed
-
- Asquith DL, Ballantine LE, Nijjar JS, Makdasy MK, Patel S, Wright PB, Reilly JH, Kerr S, Kurowska-Stolarska M, Gracie JA, McInnes IB. The liver X receptor pathway is highly upregulated in rheumatoid arthritis synovial macrophages and potentiates TLR-driven cytokine release. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72:2024–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

