Recruitment of the m6A/m6Am demethylase FTO to target RNAs by the telomeric zinc finger protein ZBTB48
- PMID: 39300486
- PMCID: PMC11414060
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-024-03392-7
Recruitment of the m6A/m6Am demethylase FTO to target RNAs by the telomeric zinc finger protein ZBTB48
Abstract
Background: N6-methyladenosine (m6A), the most abundant internal modification on eukaryotic mRNA, and N6, 2'-O-dimethyladenosine (m6Am), are epitranscriptomic marks that function in multiple aspects of posttranscriptional regulation. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) can remove both m6A and m6Am; however, little is known about how FTO achieves its substrate selectivity.
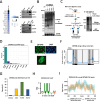
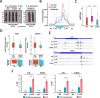
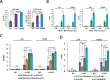
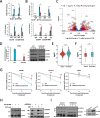
Results: Here, we demonstrate that ZBTB48, a C2H2-zinc finger protein that functions in telomere maintenance, associates with FTO and binds both mRNA and the telomere-associated regulatory RNA TERRA to regulate the functional interactions of FTO with target transcripts. Specifically, depletion of ZBTB48 affects targeting of FTO to sites of m6A/m6Am modification, changes cellular m6A/m6Am levels and, consequently, alters decay rates of target RNAs. ZBTB48 ablation also accelerates growth of HCT-116 colorectal cancer cells and modulates FTO-dependent regulation of Metastasis-associated protein 1 (MTA1) transcripts by controlling the binding to MTA1 mRNA of the m6A reader IGF2BP2.
Conclusions: Our findings thus uncover a previously unknown mechanism of posttranscriptional regulation in which ZBTB48 co-ordinates RNA-binding of the m6A/m6Am demethylase FTO to control expression of its target RNAs.
Keywords: FTO; ICLIP; M6A/m6Am; MRNA modification; RNA-binding; TERRA; TZAP; Telomeres; ZBTB48.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Chen T, Hao YJ, Zhang Y, Li MM, Wang M, Han W, et al. m(6)A RNA methylation is regulated by microRNAs and promotes reprogramming to pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16:289–301. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

