Plasma-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) as biomarkers of sepsis in burn patients via label-free Raman spectroscopy
- PMID: 39300768
- PMCID: PMC11529045
- DOI: 10.1002/jev2.12506
Plasma-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) as biomarkers of sepsis in burn patients via label-free Raman spectroscopy
Abstract
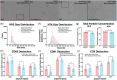
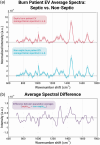
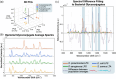
Sepsis following burn trauma is a global complication with high mortality, with ∼60% of burn patient deaths resulting from infectious complications. Diagnosing sepsis is complicated by confounding clinical manifestations of the burn injury, and current biomarkers lack the sensitivity and specificity required for prompt treatment. There is a strong rationale to assess circulating extracellular vesicles (EVs) from patient liquid biopsy as sepsis biomarkers due to their release by pathogens from bacterial biofilms and roles in the subsequent immune response. This study applies Raman spectroscopy to patient plasma-derived EVs for rapid, sensitive, and specific detection of sepsis in burn patients, achieving 97.5% sensitivity and 90.0% specificity. Furthermore, spectral differences between septic and non-septic burn patient EVs could be traced to specific glycoconjugates of bacterial strains associated with sepsis morbidity. This work illustrates the potential application of EVs as biomarkers in clinical burn trauma care and establishes Raman analysis as a fast, label-free method to specifically identify features of bacterial EVs relevant to infection amongst the host background.
Keywords: bacterial EVs (bEVs); diagnostics; exosomes; systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS).
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Update of
-
Plasma-derived Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) as Biomarkers of Sepsis in Burn Patients via Label-free Raman Spectroscopy.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 15:2024.05.14.593634. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.14.593634. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Extracell Vesicles. 2024 Sep;13(9):e12506. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12506. PMID: 38798662 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Bachurski, D. , Schuldner, M. , Nguyen, P. H. , Malz, A. , Reiners, K. S. , Grenzi, P. C. , Babatz, F. , Schauss, A. C. , Hansen, H. P. , Hallek, M. , & Pogge von Strandmann, E. (2019). Extracellular vesicle measurements with nanoparticle tracking analysis—An accuracy and repeatability comparison between NanoSight NS300 and ZetaView. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 8(1), 1596016. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bouza, E. , Onori, R. , Semiglia‐Chong, M. A. , Álvarez‐Uría, A. , Alcalá, L. , & Burillo, A. (2020). Fast track SSTI management program based on a rapid molecular test (GeneXpert® MRSA/SA SSTI) and antimicrobial stewardship. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology, and Infection, 53, 328–335. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

