A Novel Hybrid Injectable for Soft-tissue Augmentation: Analysis of Data and Practical Experience
- PMID: 39301305
- PMCID: PMC11412701
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006190
A Novel Hybrid Injectable for Soft-tissue Augmentation: Analysis of Data and Practical Experience
Abstract
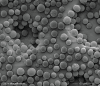
Background: HA/CaHa (HArmonyCa, Allergan Aesthetics, an AbbVie Company) is a hybrid injectable filler developed for aesthetic purposes that contains calcium hydroxyapatite microspheres suspended in a hyaluronic acid gel. This review describes preclinical and clinical data, recommendations for use based on the primary author's clinical experience, and case studies that illustrate implementation of product use recommendations and patient outcomes.
Methods: Preclinical data on the lift capacity and tissue integration of the HA/CaHa hybrid injectable and clinical data on its safety, efficacy, and real-world use were extracted from poster presentations, published literature, manufacturer instructions for use, and proprietary data files. Case studies were presented based on clinical experience.
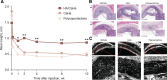
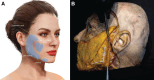
Results: The HA component of HA/CaHa provides an immediate and noticeable filling and lifting effect, whereas CaHa microspheres result in neocollagenesis. In preclinical studies, HA/CaHa demonstrated higher lift capacity (P < 0.05) and faster tissue integration than a CaHa filler and led to collagen I gene and protein expression. Clinical studies showed clinical safety and effectiveness with high patient satisfaction. The most common adverse event was injection-site response. Clinician recommendations for achieving desired aesthetic results while minimizing or preventing adverse events are reviewed, including patient selection and assessment, treatment approaches based on face shape, injection technique, and postprocedure care.
Conclusion: The novel hybrid injectable consisting of HA with incorporated CaHa microspheres in a single marketed product may help achieve aesthetic goals by immediately restoring volume and potentially improving skin architecture and soft-tissue quality over time.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Braz is a speaker, advisor and investigator for Allergan Aesthetics, an AbbVie Company. Drs. Cazerta de Paula Eduardo, Pierce, Grond, Kutikov, and Nakab are full-time employees of AbbVie. Allergan Aesthetics, an AbbVie Company, funded this work and participated in the design, research, analysis, data collection, interpretation of data, reviewing, and approval of the publication. All authors had access to relevant data and participated in the drafting, review, and approval of this publication. No honoraria or payments were made for authorship. Medical writing support was provided to the authors by Adrienne Drinkwater, PhD, and Regina Kelly, MA, of Peloton Advantage LLC, an OPEN Health Company, Parsippany, NJ, and funded by Allergan Aesthetics, an AbbVie company.
Figures



References
-
- Albert AM, Ricanek K, Jr, Patterson E. A review of the literature on the aging adult skull and face: implications for forensic science research and applications. Forensic Sci Int. 2007;172:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Wong CH, Mendelson B. Newer understanding of specific anatomic targets in the aging face as applied to injectables: aging changes in the craniofacial skeleton and facial ligaments. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;136:44S–48S. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
