SMKD: Selective Mutual Knowledge Distillation
- PMID: 39301483
- PMCID: PMC7616547
- DOI: 10.1109/IJCNN54540.2023.10191991
SMKD: Selective Mutual Knowledge Distillation
Abstract
Mutual knowledge distillation (MKD) is a technique used to transfer knowledge between multiple models in a collaborative manner. However, it is important to note that not all knowledge is accurate or reliable, particularly under challenging conditions such as label noise, which can lead to models that memorize undesired information. This problem can be addressed by improving the reliability of the knowledge source, as well as selectively selecting reliable knowledge for distillation. While making a model more reliable is a widely studied topic, selective MKD has received less attention. To address this, we propose a new framework called selective mutual knowledge distillation (SMKD). The key component of SMKD is a generic knowledge selection formulation, which allows for either static or progressive selection thresholds. Additionally, SMKD covers two special cases: using no knowledge and using all knowledge, resulting in a unified MKD framework. We present extensive experimental results to demonstrate the effectiveness of SMKD and justify its design.
Figures

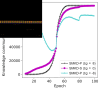
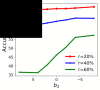
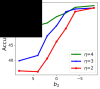
References
-
- Müller R, Kornblith S, Hinton GE. When does label smoothing help?; NeurIPS; 2019.
-
- Wang X, Hua Y, Kodirov E, Clifton DA, Robertson NM. ProSelfLC: Progressive self label correction for training robust deep neural networks; CVPR; 2021.
-
- Yuan L, Tay FE, Li G, Wang T, Feng J. Revisiting knowledge distillation via label smoothing regularization; CVPR; 2020.
-
- Wang Y, Ma X, Chen Z, Luo Y, Yi J, Bailey J. Symmetric cross entropy for robust learning with noisy labels; ICCV; 2019.
-
- Arazo E, Ortego D, Albert P, O’Connor N, Mcguinness K. Unsupervised label noise modeling and loss correction; ICML; 2019.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
