An interconnected data infrastructure to support large-scale rare disease research
- PMID: 39302238
- PMCID: PMC11413801
- DOI: 10.1093/gigascience/giae058
An interconnected data infrastructure to support large-scale rare disease research
Abstract
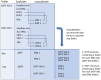
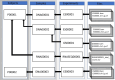
The Solve-RD project brings together clinicians, scientists, and patient representatives from 51 institutes spanning 15 countries to collaborate on genetically diagnosing ("solving") rare diseases (RDs). The project aims to significantly increase the diagnostic success rate by co-analyzing data from thousands of RD cases, including phenotypes, pedigrees, exome/genome sequencing, and multiomics data. Here we report on the data infrastructure devised and created to support this co-analysis. This infrastructure enables users to store, find, connect, and analyze data and metadata in a collaborative manner. Pseudonymized phenotypic and raw experimental data are submitted to the RD-Connect Genome-Phenome Analysis Platform and processed through standardized pipelines. Resulting files and novel produced omics data are sent to the European Genome-Phenome Archive, which adds unique file identifiers and provides long-term storage and controlled access services. MOLGENIS "RD3" and Café Variome "Discovery Nexus" connect data and metadata and offer discovery services, and secure cloud-based "Sandboxes" support multiparty data analysis. This successfully deployed and useful infrastructure design provides a blueprint for other projects that need to analyze large amounts of heterogeneous data.
Keywords: bioinformatics; computational biology; fair data; genetics; infrastructure; rare disease.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press GigaScience.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

