Sepsis-induced coagulopathy (SIC) in the management of sepsis
- PMID: 39302568
- PMCID: PMC11415329
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-024-01380-5
Sepsis-induced coagulopathy (SIC) in the management of sepsis
Abstract
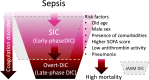
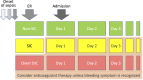
The mortality rate of sepsis remains high and further increases when complicated by disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Consequently, early detection and appropriate management of DIC will be helpful for the management of sepsis. Although overt DIC criteria are often used for diagnosing definitive DIC, it was not designed to detect early-phase DIC. The criteria and scoring system for sepsis-induced coagulopathy (SIC) were developed and introduced in 2017 to detect early-stage DIC, and they were subsequently adopted by the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis in 2019. The objective of detecting SIC was not to miss the patients at high risk of developing overt DIC at an earlier time. Although anticoagulant therapies are potential options for the treatment of sepsis-associated DIC, their effectiveness has not been established, and further research is warranted. For that purpose, an international collaborative platform is required for future clinical trials, and SIC criteria have been suggested for such studies. Calculating the SIC score is straightforward and suitable for use in clinical settings. This review aims to introduce SIC criteria and its scoring system for better management of sepsis-associated DIC. We also intended to update the current knowledge regarding this novel diagnostic criterion.
Keywords: Anticoagulants; Clinical trial; Coagulopathy; Disseminated intravascular coagulation; Sepsis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TI has participated in advisory boards of Japan Blood Products Organization, Toray Medical, and Asahi Kasei Pharmaceuticals and received a research grant from JIMRO. JH has received honoraria from Asahi Kasei, Diagnostica Stago, Pfizer PFE France and Sanofi Aventis France, MSD, Shionogi, and Inotrem. JHL serves on the Steering Committees for Merck, Octapharma, and Werfen. TI and JHL were instrumental in the creation and dissemination of the SIC and SIC scoring system. JH is an Editorial Board member of this journal.
Figures
References
-
- Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer S, Fleischmann-Struzek C, Machado FR, Reinhart KK, Rowan K, Seymour CW, Watson RS, West TE, Marinho F, Hay SI, Lozano R, Lopez AD, Angus DC, Murray CJL, Naghavi M. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: analysis for the global burden of disease study. Lancet. 2020;395(10219):200–11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iba T, Levy JH, Yamakawa K, Thachil J, Warkentin TE, Levi M, Scientific and Standardization Committee on DIC of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Proposal of a two-step process for the diagnosis of sepsis-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Thromb Haemost. 2019;17(8):1265–8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

