Molecular basis of TMED9 oligomerization and entrapment of misfolded protein cargo in the early secretory pathway
- PMID: 39303030
- PMCID: PMC11414720
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adp2221
Molecular basis of TMED9 oligomerization and entrapment of misfolded protein cargo in the early secretory pathway
Abstract
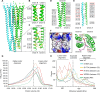
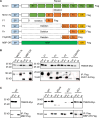
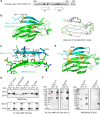
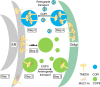
Intracellular accumulation of misfolded proteins causes serious human proteinopathies. The transmembrane emp24 domain 9 (TMED9) cargo receptor promotes a general mechanism of cytotoxicity by entrapping misfolded protein cargos in the early secretory pathway. However, the molecular basis for this TMED9-mediated cargo retention remains elusive. Here, we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of TMED9, which reveal its unexpected self-oligomerization into octamers, dodecamers, and, by extension, even higher-order oligomers. The TMED9 oligomerization is driven by an intrinsic symmetry mismatch between the trimeric coiled coil domain and the tetrameric transmembrane domain. Using frameshifted Mucin 1 as an example of aggregated disease-related protein cargo, we implicate a mode of direct interaction with the TMED9 luminal Golgi-dynamics domain. The structures suggest and we confirm that TMED9 oligomerization favors the recruitment of coat protein I (COPI), but not COPII coatomers, facilitating retrograde transport and explaining the observed cargo entrapment. Our work thus reveals a molecular basis for TMED9-mediated misfolded protein retention in the early secretory pathway.
Figures


References
-
- Dvela-Levitt M., Shaw J. L., Greka A., A rare kidney disease to cure them all? Towards mechanism-based therapies for proteinopathies. Trends Mol. Med. 27, 394–409 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Dvela-Levitt M., Kost-Alimova M., Emani M., Kohnert E., Thompson R., Sidhom E.-H., Rivadeneira A., Sahakian N., Roignot J., Papagregoriou G., Small molecule targets TMED9 and promotes lysosomal degradation to reverse proteinopathy. Cell 178, 521–535.e23 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

