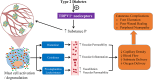
The Sensory Neuron-Mast Cell Axis Regulation of Skin Microcirculation in Diabetes: Implication for Diabetes-Related Cutaneous Complications
- PMID: 39303086
- PMCID: PMC11417433
- DOI: 10.2337/dbi24-0035
The Sensory Neuron-Mast Cell Axis Regulation of Skin Microcirculation in Diabetes: Implication for Diabetes-Related Cutaneous Complications
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment on
-
A Neuron-Mast Cell Axis Regulates Skin Microcirculation in Diabetes.Diabetes. 2024 Oct 1;73(10):1728-1741. doi: 10.2337/db23-0862. Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38833271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roustit M, Cracowski J-L. Non-invasive assessment of skin microvascular function in humans: an insight into methods. Microcirculation 2012;19:47–64 - PubMed
-
- Serné EH, IJzerman RG, Gans ROB, et al. Direct evidence for insulin-induced capillary recruitment in skin of healthy subjects during physiological hyperinsulinemia. Diabetes 2002;51:1515–1522 - PubMed
-
- Meijer RI, De Boer MP, Groen MR, et al. Insulin-induced microvascular recruitment in skin and muscle are related and both are associated with whole-body glucose uptake. Microcirculation 2012;19:494–500 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources