Adjuvant Nivolumab for Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma at High Risk of Recurrence After Nephrectomy: Part B of the Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase III CheckMate 914 Trial
- PMID: 39303200
- PMCID: PMC11709003
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.24.00773
Adjuvant Nivolumab for Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma at High Risk of Recurrence After Nephrectomy: Part B of the Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase III CheckMate 914 Trial
Abstract
Purpose: CheckMate 914 is a two-part, randomized phase III trial evaluating adjuvant nivolumab plus ipilimumab (part A) or adjuvant nivolumab monotherapy (part B) versus placebo in mutually exclusive populations of patients with localized renal cell carcinoma (RCC) at high risk of postnephrectomy recurrence. Part A showed no disease-free survival (DFS) benefit for adjuvant nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus placebo. We report results from part B.
Methods: Patients were randomly assigned (2:1:1) to nivolumab (240 mg once every 2 weeks for up to 12 doses), placebo, or nivolumab (240 mg once every 2 weeks for up to 12 doses) plus ipilimumab (1 mg/kg once every 6 weeks for up to four doses). The planned treatment duration was 24 weeks (approximately 5.5 months). The primary end point was DFS per blinded independent central review (BICR) for nivolumab versus placebo; safety was a secondary end point.
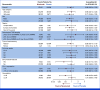
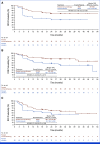
Results: Overall, 825 patients were randomly assigned to nivolumab (n = 411), placebo (n = 208), or nivolumab plus ipilimumab (n = 206). With a median follow-up of 27.0 months (range, 18.0-42.4), the primary end point of improved DFS per BICR with nivolumab versus placebo was not met (hazard ratio [HR], 0.87 [95% CI, 0.62 to 1.21]; P = .40); the median DFS was not reached in either arm, and 18-month DFS rates were 78.4% versus 75.4%. The HR for DFS per investigator was 0.80 (95% CI, 0.58 to 1.12; P = .19). Grade 3-4 all-cause adverse events (AEs) occurred in 17.2%, 15.0%, and 28.9% of patients with nivolumab, placebo, and nivolumab plus ipilimumab, respectively. Any-grade treatment-related AEs led to discontinuation in 9.6%, 1.0%, and 28.4%, respectively.
Conclusion: Part B of CheckMate 914 did not meet the primary end point of improved DFS for nivolumab versus placebo in patients with localized RCC at high risk of postnephrectomy recurrence.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03138512.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures


References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) : Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Kidney cancer—Version 1.2024. 2023. https://www.nccn.org - PubMed
-
- Escudier B, Porta C, Schmidinger M, et al. : Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 30:706-720, 2019 - PubMed
-
- Ravaud A, Motzer RJ, Pandha HS, et al. : Adjuvant sunitinib in high-risk renal-cell carcinoma after nephrectomy. N Engl J Med 375:2246-2254, 2016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

