Therapeutic single-cell landscape: methotrexate exacerbates interstitial lung disease by compromising the stemness of alveolar epithelial cells under systemic inflammation
- PMID: 39303666
- PMCID: PMC11437874
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105339
Therapeutic single-cell landscape: methotrexate exacerbates interstitial lung disease by compromising the stemness of alveolar epithelial cells under systemic inflammation
Abstract
Background: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) poses a serious threat in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the impact of cornerstone drugs, including methotrexate (MTX) and TNF inhibitor, on RA-associated ILD (RA-ILD) remains controversial.
Methods: Using an SKG mouse model and single-cell transcriptomics, we investigated the effects of MTX and TNF blockade on ILD.
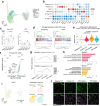
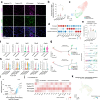
Findings: Our study revealed that MTX exacerbates pulmonary inflammation by promoting immune cell infiltration, Th17 activation, and fibrosis. In contrast, TNF inhibitor ameliorates these features and inhibits ILD progression. Analysis of data from a human RA-ILD cohort revealed that patients with ILD progression had persistently higher systemic inflammation than those without progression, particularly among the subgroup undergoing MTX treatment.
Interpretation: These findings highlight the need for personalized therapeutic approaches in RA-ILD, given the divergent outcomes of MTX and TNF inhibitor.
Funding: This work was funded by GENINUS Inc., and the National Research Foundation of Korea, and Seoul National University Hospital.
Keywords: Fibrosis; Macrophage differentiation; Methotrexate; Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease; SKG mouse; Th17 cell activation; Tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Dr. Sparks has received research support from Bristol Myers Squibb and Boehringer Ingelheim unrelated to this work. He has performed consultancy for AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead, Inova Diagnostics, Janssen, Optum, Pfizer, ReCor, Sobi, and UCB unrelated to this work.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

