Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of pulmonary and extrapulmonary cryptococcosis
- PMID: 39304813
- PMCID: PMC11414175
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-024-09895-9
Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of pulmonary and extrapulmonary cryptococcosis
Abstract
Background: Cryptococcosis is progressively acknowledged among people, irrespective of the human with or without immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This change in epidemiology has been recorded in recent years, prompting closer examination and a broader understanding of the disease manifestations and risk factors.
Methods: The data of cryptococcal infections in China during 11 years were retrospectively analyzed. According to the position of infection, the patients were categorized into the pulmonary infection group and extrapulmonary infection group. The composition of the two groups was compared, and the potential risk factors of disseminated infection were analyzed. Logistic regression was used to analyze the prognostic risk factors of the disease.
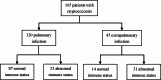
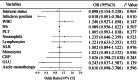
Results: A total of 165 patients were enrolled. 113 (68.5%) were male, and the age was 47.49 (18-82) years. 101 cases (61.2%) had a normal immune function and 64 cases (38.8%) had impaired immune function. 45 patients had extrapulmonary infection, involving the central nervous system, bone and joint, skin and bloodstream, and 120 patients had simple pulmonary infection. The mortality of the extrapulmonary infection group (48.9%) was significantly higher than that of the pulmonary infection group (0.8%). According to univariate logistic regression analysis, immune status (hazard ratio [HR], 4.476; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.725-11.618; P = 0.002), infection position ([HR], 113.826; [CI], 14.607-886.967; P < 0.001), white blood cell count, ([HR],1.209;[CI], 1.054-1.386; P = 0.007), hemoglobin ([HR], 0.970; [CI], 0.955-0.986; P < 0.001), platelet count ([HR], 0.993; [CI], 0.987-0.999; P = 0.026), neutrophil percentage ([HR], 1.115; [CI], 1.065-1.168; P < 0.001), lymphocyte percentage ([HR], 0.875; [CI], 0.827-0.927; P < 0.001), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) ([HR], 1.144; [CI], 1.072-1.221; P < 0.001), monocyte percentage ([HR], 0.752; [CI], 0.618-0.915; P = 0.004) were related to the prognosis. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the infection position was remained related to the prognosis with statistical significance ([HR], 0.018; [CI], 0.001-0.384; P = 0.001).
Conclusion: Extrapulmonary infection of Cryptococcosis is an important risk factor for prognosis. High levels of neutrophils and NLR, and low levels of lymphocytes and monocytes may lead to disseminated infection of Cryptococcosis. Further studies are needed to reduce the occurrence rate of extrapulmonary infection and mortality.
Keywords: Cryptococcus; Extrapulmonary infection; Prognosis; Pulmonary infection.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Longitudinal clinical findings and outcome among patients with Cryptococcus gattii infection in British Columbia.Clin Infect Dis. 2015 May 1;60(9):1368-76. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ041. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Clin Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25632012
-
Cryptococcosis in patients with liver cirrhosis: Death risk factors and predictive value of prognostic models.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2021 Oct;20(5):460-468. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2021.06.006. Epub 2021 Jun 26. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2021. PMID: 34233849
-
[Clinical analysis of pulmonary cryptococcosis in non-human immunodeficiency virus infection patients].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018 Oct 18;50(5):855-860. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018. PMID: 30337748 Chinese.
-
Retrospective analysis of pulmonary cryptococcosis and extrapulmonary cryptococcosis in a chinese tertiary hospital.BMC Pulm Med. 2023 Jul 27;23(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02578-2. BMC Pulm Med. 2023. PMID: 37501136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinicopathological features of isolated pulmonary cryptococcosis in HIV-negative patients.J Int Med Res. 2020 Jun;48(6):300060520927877. doi: 10.1177/0300060520927877. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32527202 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Incidence and prognostic factors for pulmonary infection complications in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Jul 15;17(7):5371-5384. doi: 10.62347/KERT9218. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40821054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suwatanapongched T, Sangsatra W, Boonsarngsuk V, Watcharananan SP, Incharoen P. Clinical and radiologic manifestations of pulmonary cryptococcosis in immunocompetent patients and their outcomes after treatment. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2013;19(6):438–46. - PubMed
-
- Sun L, Chen H, Shao C, Song Y, Bai C. Pulmonary cryptococcosis with trachea wall invasion in an immunocompetent patient: a case report and literature review. Respiration. 2014;87(4):324–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources