Hsa_circ_0006010 and hsa_circ_0002903 in peripheral blood serve as novel diagnostic, surveillance and prognostic biomarkers for disease progression in chronic myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 39304860
- PMCID: PMC11414102
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12943-x
Hsa_circ_0006010 and hsa_circ_0002903 in peripheral blood serve as novel diagnostic, surveillance and prognostic biomarkers for disease progression in chronic myeloid leukemia
Abstract
Background: In the era of tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) treatment, the progression of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) remains a significant clinical challenge, and genetic biomarkers for the early identification of CML patients at risk for progression are limited. This study explored whether essential circular RNAs (circRNAs) can be used as biomarkers for diagnosing and monitoring CML disease progression and assessing CML prognosis.
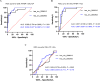
Methods: Peripheral blood (PB) samples were collected from 173 CML patients (138 patients with chronic phase CML [CML-CP] and 35 patients with accelerated phase/blast phase CML [CML-AP/BP]) and 63 healthy controls (HCs). High-throughput RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) was used to screen dysregulated candidate circRNAs for a circRNA signature associated with CML disease progression. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used for preliminary verification and screening of candidate dysregulated genes, as well as subsequent exploration of clinical applications. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, Spearman's rho correlation test, and the Kaplan-Meier method were used for statistical analysis.
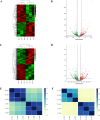
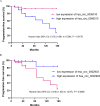
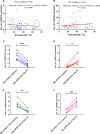
Results: The aberrant expression of hsa_circ_0006010 and hsa_circ_0002903 during CML progression could serve as valuable biomarkers for differentiating CML-AP/BP patients from CMP-CP patients or HCs. In addition, the expression levels of hsa_circ_0006010 and hsa_circ_0002903 were significantly associated with the clinical features of CML patients but were not directly related to the four scoring systems. Furthermore, survival analysis revealed that high hsa_circ_0006010 expression and low hsa_circ_0002903 expression indicated poor progression-free survival (PFS) in CML patients. Finally, PB hsa_circ_0006010 and hsa_circ_0002903 expression at diagnosis may also serve as disease progression surveillance markers for CML patients but were not correlated with PB BCR-ABL1/ABL1IS.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated that PB levels of hsa_circ_0006010 and hsa_circ_0002903 may serve as novel diagnostic, surveillance, and prognostic biomarkers for CML disease progression and may contribute to assisting in the diagnosis of CML patients at risk for progression and accurate management of advanced CML patients.
Keywords: Chronic myeloid leukemia; Diagnosis; Disease progression; Hsa_circ_0002903; Hsa_circ_0006010; Prognostic biomarkers; Surveillance.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Y20220123 and Y20220744/the Basic Scientific Research Project of Wenzhou City
- Y20220123 and Y20220744/the Basic Scientific Research Project of Wenzhou City
- 2021KY216/the Medical and Health Research Science and Technology Plan Project of Zhejiang Province
- LGF20H200005/the Basic Public Welfare Technology Research Project of Zhejiang Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

