Educational differences in years lived with disability due to mental and substance use disorders: a cohort study using nationwide Norwegian and Danish registries
- PMID: 39304880
- PMCID: PMC11416009
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-024-20064-0
Educational differences in years lived with disability due to mental and substance use disorders: a cohort study using nationwide Norwegian and Danish registries
Abstract
Background: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study have shown that the burden of mental and substance use disorders is considerable, and unevenly distributed across demographic groups in the population. However, there is a lack of knowledge on how this burden differs by socioeconomic position. The aim of this study was to examine educational differences in years lived with disability (YLDs) from mental and substance use disorders among males and females in two high-income countries, taking comorbidity with other diseases into account.
Methods: The study included all registered residents in Denmark and Norway from 2011 to 2021. Diagnostic information was retrieved from records in the Norwegian National Patient Registry (NPR) and the Danish Psychiatric Central Research Register (PCRR) and used as proxy measures for disorder prevalence. Demographical and educational information was taken from administrative registries. The YLD is a measure of the non-fatal health loss in the population and was calculated by multiplying the duration of a disorder with a disability weight (DW), scaled between 0 and 1. Information on remission and DWs were retrieved from the GBD study and other sources, and disorder specific DWs were averaged by severity levels and adjusted for comorbidity.
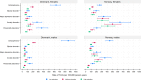
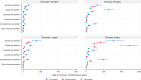
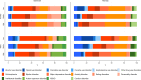
Results: Educational gradients in YLD rates were found for mental and substance disorders overall, and for most of the specific disorders. The educational gradient was more pronounced for schizophrenia, intellectual disability and substance use disorders than for eating, anxiety, and affective disorders. Both higher YLD rates, and a larger attributed proportion of the total YLDs, were found for schizophrenia, intellectual disability, and substance use disorders in the groups with low versus high education. YLD rates for eating, anxiety, and affective disorders were more equal across educational levels, but constituted a smaller proportion of the total YLDs among the groups with low versus the groups with high educational level.
Conclusion: Most of the disease burden related to mental and substance use disorders falls on those with the fewest years of education. This should be taken into consideration when public health targets aimed at improving mental health and reducing social inequalities in health are developed and implemented.
Keywords: Disease burden; Educational gradient; Mental disorders; Substance use disorders.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- GBD 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the global burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. 2024;403(10440):2133–61. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Enroth L, Jasilionis D, Nemeth L, Strand BH, Tanjung I, Sundberg L, Fors S, Jylha M, Bronnum-Hansen H. Changes in socioeconomic differentials in old age life expectancy in four nordic countries: the impact of educational expansion and education-specific mortality. Eur J Ageing. 2022;19(2):161–73. - PMC - PubMed
-
- The Norwegian Ministry of Health and Care Services: Meld. St. 15. (2022–2023) Folkehelsemeldinga — Nasjonal strategi for utjamning av sosiale helseforskjellar [Public Health Report - National strategy for equalizing social differences in health]. Helse- og omsorgsdepartementet; 2023.
-
- Demange PA, Boomsma DI, van Bergen E, Nivard MG. Evaluating the causal relationship between educational attainment and mental health. medRxiv 2024.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

