Clinical value of peripheral blood miR-21 and miR-486 combined with CT forearly cancer diagnosis in pulmonary nodulessmoking
- PMID: 39304898
- PMCID: PMC11414282
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-024-03028-8
Clinical value of peripheral blood miR-21 and miR-486 combined with CT forearly cancer diagnosis in pulmonary nodulessmoking
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the clinical significance of combining peripheral blood miR-21 and miR-486 with CT for the early cancer diagnosis in pulmonary nodules.
Methods: A total of 215 patients diagnosed with isolated pulmonary nodules with a history of smoking were selected as researchsubjects. 30 healthy volunteers with a history of smoking were recruitedas the control group.The selection of subjectswas based on the presence of isolated pulmonary nodules detected on chest CT scans. The training set consisted of 65 patients with lung nodules and 30 healthy smokers, while the verification setincluded 150 patients with lung nodules.
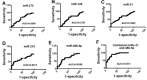
Results: Compared with the control group, the plasma expression level of miR-210 was significantly higher in the group of patients with benign pulmonary nodules (P < 0.05). The level of miR-486-5p was lower in patients with malignant pulmonary nodules compared to those with benign pulmonary nodules (P < 0.05). Moreover, the plasma level of miR-210was higher in patients with malignant pulmonary nodules compared to those with benign pulmonary nodules and healthy smokers (P < 0.05). The combination of miR-21 and miR-486 yielded an AUC of 0.865, which was significantly higher than any other gene combination (95%CI: 0.653-0.764, P < 0.05).
Conclusions: This study offered preliminary evidence supporting the use of peripheral blood miR-21 and miR-486, combined with CT scans, as potential biomarkers for the early cancer diagnosis in lung nodules.
Keywords: Early CT diagnosis; Peripheral blood; Pulmonary nodules; miR-21 and miR-486.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Highly Sensitive and Specific Panels of Plasma Exosomal microRNAs for Identification of Malignant Pulmonary Nodules.Clin Respir J. 2024 Nov;18(11):e70034. doi: 10.1111/crj.70034. Clin Respir J. 2024. PMID: 39548655 Free PMC article.
-
Combining serum miRNAs, CEA, and CYFRA21-1 with imaging and clinical features to distinguish benign and malignant pulmonary nodules: a pilot study : Xianfeng Li et al.: Combining biomarker, imaging, and clinical features to distinguish pulmonary nodules.World J Surg Oncol. 2017 May 25;15(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12957-017-1171-y. World J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28545454 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of lung cancer in individuals with solitary pulmonary nodules by plasma microRNA biomarkers.BMC Cancer. 2011 Aug 24;11:374. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-374. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21864403 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Patient With a Pulmonary Nodule: A Review.JAMA. 2022 Jan 18;327(3):264-273. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.24287. JAMA. 2022. PMID: 35040882 Review.
-
[Diagnostic work-up of pulmonary nodules : Management of pulmonary nodules detected with low‑dose CT screening].Radiologe. 2016 Sep;56(9):803-9. doi: 10.1007/s00117-016-0150-6. Radiologe. 2016. PMID: 27495787 Review. German.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA‑21: A potential therapeutic target in lung cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2025 Aug;67(2):67. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5773. Epub 2025 Jul 11. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40641110 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen R, Zhang C, Cheng Y, et al. LncRNA UCC promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the miR-143-3p/SOX5 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Lab Invest. 2021;101:1153–65. - PubMed
-
- Ge N, Mao C, Yang Q, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism rs3746444 in miR-499a affects susceptibility to nonsmall cell lung carcinoma by regulating the expression of CD200[J]. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43:2221–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical