Synthesis of new binary trimethoxyphenylfuran pyrimidinones as proficient and sustainable corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in acidic medium: experimental, surface morphology analysis, and theoretical studies
- PMID: 39304940
- PMCID: PMC11414101
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-024-01280-6
Synthesis of new binary trimethoxyphenylfuran pyrimidinones as proficient and sustainable corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in acidic medium: experimental, surface morphology analysis, and theoretical studies
Abstract
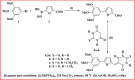
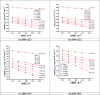
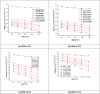
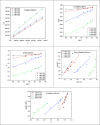
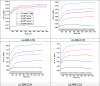
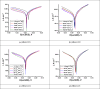
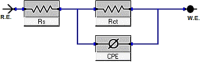
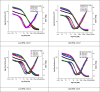
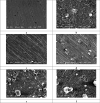
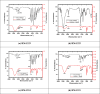
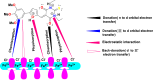
In this study, synthesis and assessment of the corrosion inhibition of four new binary heterocyclic pyrimidinones on CS in 1.0 M hydrochloric acid solutions at various temperatures (30-50 °C) were investigated. The synthesized molecules were designed and synthesized through Suzuki coupling reaction, the products were identified as 5-((5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)furan-2-yl)methylene)pyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione (HM-1221), 2-thioxo-5-((5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)furan-2-yl)methylene)dihydropyrimidine-4,6(1H,5H)-dione (HM-1222), 1,3-diethyl-2-thioxo-5-((5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)furan-2-yl)methylene)dihydropyrimidine-4,6(1H,5H)-dione (HM-1223) and 1,3-dimethyl-5-((5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)furan-2-yl)methylene)pyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione (HM-1224). The experiments include weight loss measurements (WL), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and potentiodynamic polarization (PDP). From the measurements, it can be shown that the inhibition efficiency (η) of these organic derivatives increases with increasing the doses of inhibitors. The highest η recorded from EIS technique were 89.3%, 90.0%, 92.9% and 89.7% at a concentration of 11 × 10-6 M and 298 K for HM-1221, HM-1222, HM-1223, and HM-1224, respectively. The adsorption of the considered derivatives fit to the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. Since the ΔGoads values were found to be between - 20.1 and - 26.1 kJ mol-1, the analyzed isotherm plots demonstrated that the adsorption process for these derivatives on CS surface is a mixed-type inhibitors. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), atomic force microscope (AFM) and Fourier- transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) were utilized to study the surface morphology, whereby, quantum chemical analysis can support the mechanism of inhibition. DFT data and experimental findings were found in consistent agreement.
Keywords: Carbon steel; Corrosion inhibition; Pyrimidinone derivatives; Quantum chemical calculations.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Rajput A, Paik JK. Effects of naturally-progressed corrosion on the chemical and mechanical properties of structural steels. Structures. 2021;29:2120–38. - DOI
-
- Vecchi F, Franceschini L, Tondolo F, Belletti B, Montero JS, Minetola P. Corrosion morphology of prestressing steel strands in naturally corroded PC beams. Constr Build Mater. 2021;296: 123720. - DOI
-
- Ettahiri W, Adardour M, Ech-chihbi E, Azam M, Salim R, Dalbouha S, Min K, Rais Z, Baouid A, Taleb M. 1,2,3-triazolyl-linked benzimidazolone derivatives as new eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in 1 M HCl solution: experimental and computational studies. Colloids Surf. 2024;681: 132727. - DOI
-
- Aslam R, Mobin M, Zehra S, Aslam J. A comprehensive review of corrosion inhibitors employed to mitigate stainless steel corrosion in different environments. J Mol Liq. 2022;364: 119992. - DOI
-
- Wu T, Zhang K. Corrosion and protection of magnesium alloys: recent advances and future perspectives. Coatings. 2023;13(9):1533. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
