Intestinal deguelin drives resistance to acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in female mice
- PMID: 39305468
- PMCID: PMC11418218
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2404138
Intestinal deguelin drives resistance to acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in female mice
Abstract
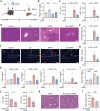
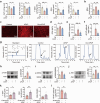
Acetaminophen (APAP) overdose is a leading cause of drug-induced liver injury (DILI), with gender-specific differences in susceptibility. However, the mechanism underlying this phenomenon remains unclear. Our study reveals that the gender-specific differences in susceptibility to APAP-induced hepatotoxicity are due to differences in the gut microbiota. Through microbial multi-omics and cultivation, we observed increased gut microbiota-derived deguelin content in both women and female mice. Administration of deguelin was capable of alleviating hepatotoxicity in APAP-treated male mice, and this protective effect was associated with the inhibition of hepatocyte oxidative stress. Mechanistically, deguelin reduced the expression of thyrotropin receptor (TSHR) in hepatocytes with APAP treatment through direct interaction. Pharmacologic suppression of TSHR expression using ML224 significantly increased hepatic glutathione (GSH) in APAP-treated male mice. These findings suggest that gut microbiota-derived deguelin plays a crucial role in reducing APAP-induced hepatotoxicity in female mice, offering new insights into therapeutic strategies for DILI.
Keywords: DILI; deguelin; gender variability; gut microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
