Fundamentals and Exceptions of the LysR-type Transcriptional Regulators
- PMID: 39306765
- PMCID: PMC11495319
- DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.4c00219
Fundamentals and Exceptions of the LysR-type Transcriptional Regulators
Abstract
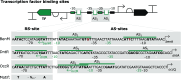
LysR-type transcriptional regulators (LTTRs) are emerging as a promising group of macromolecules for the field of biosensors. As the largest family of bacterial transcription factors, the LTTRs represent a vast and mostly untapped repertoire of sensor proteins. To fully harness these regulators for transcription factor-based biosensor development, it is crucial to understand their underlying mechanisms and functionalities. In the first part, this Review discusses the established model and features of LTTRs. As dual-function regulators, these inducible transcription factors exude precise control over their regulatory targets. In the second part of this Review, an overview is given of the exceptions to the "classic" LTTR model. While a general regulatory mechanism has helped elucidate the intricate regulation performed by LTTRs, it is essential to recognize the variations within the family. By combining this knowledge, characterization of new regulators can be done more efficiently and accurately, accelerating the expansion of transcriptional sensors for biosensor development. Unlocking the pool of LTTRs would significantly expand the currently limited range of detectable molecules and regulatory functions available for the implementation of novel synthetic genetic circuitry.
Keywords: LysR-type transcriptional regulators; biosensors; genetic circuitry; prokaryotes; synthetic biology; transcription factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

