Toxic epidermal necrolysis following heart transplantation may caused by cefoperazone sodium and sulbactam sodium
- PMID: 39307887
- PMCID: PMC11418188
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-024-03025-x
Toxic epidermal necrolysis following heart transplantation may caused by cefoperazone sodium and sulbactam sodium
Abstract
Background: The outcome of heart transplantation is significantly affected by perioperative infections. Individualised immunosuppression strategies are essential to reduce the risk of such infections.
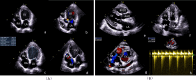
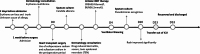
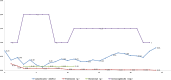
Case presentation: We report the successful management of a 56-year-old male patient diagnosed with dilated cardiomyopathy who underwent heart transplantation. During the perioperative period, the patient was prescribed cefoperazone sodium and sulbactam sodium, which induced a severe skin reaction: toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). The patient was treated with prednisone, immunoglobulins, etanercept, and other active immunomodulatory measures, together with an individualised anti-rejection regimen and physical therapy. The systemic rash resolved within a month, and the patient was successfully discharged after surgery.
Conclusion: Effective management of heart transplantation necessitates balancing immunosuppression and infection prevention. Individualised immunosuppressive strategies are critical for optimal clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Cefoperazone sodium and sulbactam sodium; Drug-induced dermatitis; Heart transplantation; Immunosuppression; Toxic epidermal necrolysis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Velleca A, Shullo MA, Dhital K. Et. The International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) guidelines for the care of heart transplant recipients. J Heart Lung Transpl. 2023;42(5):e1–141. - PubMed
-
- Lerch M, Mainetti C, Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli B. Current perspectives on Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;54(1):147–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

