Self-Assembly of Soft and Conformable Broadband Absorbing Nanocellulose-Gold Nanoparticle Composites
- PMID: 39307969
- PMCID: PMC11450681
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c10244
Self-Assembly of Soft and Conformable Broadband Absorbing Nanocellulose-Gold Nanoparticle Composites
Abstract
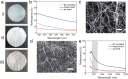
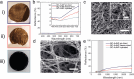
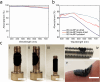
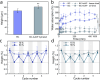
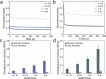
Broadband light-absorbing materials are of large interest for numerous applications ranging from solar harvesting and photocatalysis to low reflection coatings. Fabrication of these materials is often complex and typically utilizes coating techniques optimized for flat and hard materials. Here, we show a self-assembly based strategy for generating robust but mechanically flexible broadband light-absorbing soft materials that can conform to curved surfaces and surface irregularities. The materials were fabricated by adsorbing large quantities of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) on the nanofibrils of hydrated bacterial cellulose (BC) membranes by tailoring the interaction potential between the cellulose nanofibrils and the AuNPs. The highly efficient self-assembly process resulted in very dense multilayers of AuNPs on the nanofibrils, causing extensive broadening of the localized surface plasmon resonance band and a striking black appearance of the BC membranes. The nanocomposite materials showed an absorptance >96% in both the visible and the near-infrared wavelength range. The AuNP-functionalized BC membranes demonstrated excellent conformability to curved and structured surfaces and could adopt the shape of highly irregular surface structures without any obvious changes in their optical properties. The proposed self-assembly based strategy enables the fabrication of soft and conformable broadband light-absorbing nanocomposites with unique optical and mechanical properties using sustainable cellulose-based materials.
Keywords: absorptance; gold nanoparticles; nanocellulose; nanocomposite; plasmonic materials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Panagiotopoulos N. T.; Diamanti E. K.; Koutsokeras L. E.; Baikousi M.; Kordatos E.; Matikas T. E.; Gournis D.; Patsalas P. Nanocomposite Catalysts Producing Durable, Super-Black Carbon Nanotube Systems: Applications in Solar Thermal Harvesting. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 10475–10485. 10.1021/nn304531k. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhou L.; Tan Y.; Wang J.; Xu W.; Yuan Y.; Cai W.; Zhu S.; Zhu J. 3D Self-Assembly of Aluminium Nanoparticles for Plasmon-Enhanced Solar Desalination. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 393–398. 10.1038/nphoton.2016.75. - DOI
-
- Oh J.; Deutsch T. G.; Yuan H. C.; Branz H. M. Nanoporous Black Silicon Photocathode for H2 Production by Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1690–1694. 10.1039/c1ee01124c. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

