Solitary Experience and Problematic Social Media Use Among Young Adults: A Systematic Review with Recommendations for Future Research
- PMID: 39309023
- PMCID: PMC11411510
- DOI: 10.36131/cnfioritieditore20240405
Solitary Experience and Problematic Social Media Use Among Young Adults: A Systematic Review with Recommendations for Future Research
Abstract
Objective: This study was conducted to summarize existing studies on the association between solitary experiences and problematic social media use (PSMU) among young adults.
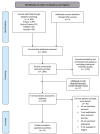
Method: A systematic review was performed according to the PRISMA guidelines, implemented in Scopus, Web of Science, PubMed and PsycINFO. We selected studies if they presented original data, assessed solitary experiences and PSMU in young adults (i.e., 18-30 age range), were published in peer reviewed journals between 2004 and 2023, and were written in English.
Results: After duplicate removal, 1,841 eligible studies were found. From these, 12 articles were selected, encompassing 4,009 participants. Most studies showed a positive association between general loneliness and PSMU. Some of these suggested that this relationship varies based on the facets of loneliness, other potential variables, and the type of social media. No mediating factors were found. Few studies assessed solitary experiences other than general loneliness, highlighting the need for a multidimensional perspective on solitary experience in investigating PSMU.
Conclusions: Implications and future research orientations are discussed.
Keywords: aloneness; loneliness; problematic social media use; social media; solitary experience; solitude.
© 2024 Giovanni Fioriti Editore s.r.l.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
Figures
References
-
- Adamczyk, K. (2018). Direct and indirect effects of relationship status through unmet need to belong and fear of being single on young adults’ romantic loneliness. Personality and Individual Differences, 124, 124–129. 10.1016/j.paid.2017.12.011 - DOI
-
- Ahmed, E., & Vaghefi, I. (2021). Social media addiction: A systematic review through cognitive-behavior model of pathological use. In Proceedings of the 54th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, 6681–6690. http://hdl.handle.net/10125/71422
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2022). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed., text rev.). 10.1176/appi.books.9780890425787 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources