Discovery and evaluation of a novel 18F-labeled vasopressin 1a receptor PET ligand with peripheral binding specificity
- PMID: 39309503
- PMCID: PMC11413668
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.05.033
Discovery and evaluation of a novel 18F-labeled vasopressin 1a receptor PET ligand with peripheral binding specificity
Abstract
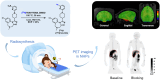
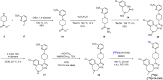
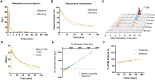
The arginine-vasopressin (AVP) hormone plays a pivotal role in regulating various physiological processes, such as hormone secretion, cardiovascular modulation, and social behavior. Recent studies have highlighted the V1a receptor as a promising therapeutic target. In-depth insights into V1a receptor-related pathologies, attained through in vivo imaging and quantification in both peripheral organs and the central nervous system (CNS), could significantly advance the development of effective V1a inhibitors. To address this need, we develop a novel V1a-targeted positron emission tomography (PET) ligand, [18F]V1A-2303 ([18F]8), which demonstrates favorable in vitro binding affinity and selectivity for the V1a receptor. Specific tracer binding in peripheral tissues was also confirmed through rigorous cell uptake studies, autoradiography, biodistribution assessments. Furthermore, [18F]8 was employed in PET imaging and arterial blood sampling studies in healthy rhesus monkeys to assess its brain permeability and specificity, whole-body distribution, and kinetic properties. Our research indicated [18F]8 as a valuable tool for noninvasively studying V1a receptors in peripheral organs, and as a foundational element for the development of next-generation, brain-penetrant ligands specifically designed for the CNS.
Keywords: Autism; Fluorine 18; Kinetic modeling; PET imaging; Positron emission tomography; Radiolabeling; V1a receptor; Vasopressin.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures





References
-
- Koshimizu T.A., Nakamura K., Egashira N., Hiroyama M., Nonoguchi H., Tanoue A. Vasopressin V1a and V1b receptors: from molecules to physiological systems. Physiol Rev. 2012;92:1813–1864. - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara Y., Tanoue A., Tsujimoto G., Koshimizu T.A. The roles of V1a vasopressin receptors in blood pressure homeostasis: a review of studies on V1a receptor knockout mice. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011;16:30–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

