An Evasive Liver Mass in a Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-Positive Patient
- PMID: 39310052
- PMCID: PMC11415121
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.0000000000001481
An Evasive Liver Mass in a Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-Positive Patient
Abstract
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is an autoimmune syndrome that is characterized by elevated levels of serum IgG4 and infiltration of various tissue types by IgG4 immunoreactive plasma cells. The IgG4-RD can result in systemic disease and the formation of inflammatory mass lesions, frequently addressed as pseudotumors. While IgG4-RD can manifest in various organs, liver involvement is rare, and because it is an immune-mediated inflammatory process, it is uncommon in patients who are immunocompromised. Furthermore, despite IgG4-RD responding well to immunosuppressive treatment, cases of spontaneous remission are exceedingly rare in the literature. In this report, we present the unique case of a self-resolving IgG4-RD lesion of the liver in a HIV positive patient.
Keywords: IgG4-related disease; immunosuppression; pseudotumor.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Figures
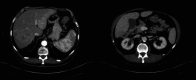
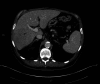
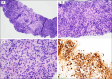

References
-
- Perugino CA, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease: An update on pathophysiology and implications for clinical care. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(12):702–14. - PubMed
-
- Umehara H, Okazaki K, Kawa S, et al. The 2020 revised comprehensive diagnostic (RCD) criteria for IgG4-RD. Mod Rheumatol. 2021;31(3):529–33. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

