Glucocorticoid therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome: Current concepts
- PMID: 39310055
- PMCID: PMC11411438
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jointm.2024.02.002
Glucocorticoid therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome: Current concepts
Abstract
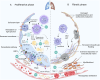
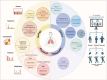
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a fatal critical disease, is induced by various insults. ARDS represents a major global public health burden, and the management of ARDS continues to challenge healthcare systems globally, especially during the pandemic of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). There remains no confirmed specific pharmacotherapy for ARDS, despite advances in understanding its pathophysiology. Debate continues about the potential role of glucocorticoids (GCs) as a promising ARDS clinical therapy. Questions regarding GC agent, dose, and duration in patients with ARDS need to be answered, because of substantial variations in GC administration regimens across studies. ARDS heterogeneity likely affects the therapeutic actions of exogenous GCs. This review includes progress in determining the GC mechanisms of action and clinical applications in ARDS, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: Acute respiratory distress syndrome; COVID-19; Clinical trials; Glucocorticoids; Heterogeneity; Steroids.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome versus classical acute respiratory distress syndrome (a narrative review).Iran J Microbiol. 2021 Dec;13(6):737-747. doi: 10.18502/ijm.v13i6.8072. Iran J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 35222850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological principles guiding prolonged glucocorticoid treatment in ARDS.Intensive Care Med. 2020 Dec;46(12):2284-2296. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06289-8. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Intensive Care Med. 2020. PMID: 33150472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation, Thrombosis, and Destruction: The Three-Headed Cerberus of Trauma- and SARS-CoV-2-Induced ARDS.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 25;11:584514. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.584514. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33101314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the pathophysiology of typical acute respiratory distress syndrome and severe COVID-19.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2022 Apr;16(4):437-446. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2022.2057300. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 35341424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacotherapy consideration of thrombolytic medications in COVID-19-associated ARDS.J Intensive Care. 2022 Jul 30;10(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s40560-022-00625-4. J Intensive Care. 2022. PMID: 35908022 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Neutrophils in ARDS.Cells. 2025 Jul 25;14(15):1151. doi: 10.3390/cells14151151. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40801583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by demulsifier poisoning: A case report.World J Radiol. 2024 Nov 28;16(11):689-695. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i11.689. World J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 39635314 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Regulation in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Implications for Inflammation and Oxidative Stress.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025 Feb 18;20:373-388. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S491687. eCollection 2025. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025. PMID: 39991071 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van der Ven F.L.I.M., Valk C.M.A., Blok S., Brouwer M.G., Go D.M., Lokhorst A., et al. Broadening the Berlin definition of ARDS to patients receiving high-flow nasal oxygen: an observational study in patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure due to COVID-19. Ann Intensive Care. 2023;13(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13613-023-01161-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

