Evaluating the Depth of Penetration of Calcium Hydroxide Mixed With Three Different Herbal Essential Oils Using a Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope
- PMID: 39310401
- PMCID: PMC11415001
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.67414
Evaluating the Depth of Penetration of Calcium Hydroxide Mixed With Three Different Herbal Essential Oils Using a Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope
Abstract
Introduction The goal of endodontic therapy is to completely eliminate the infection and stop microbes from infecting or reinfecting the root canal and the periradicular tissues. Amongst the primary microorganisms, Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis), a Gram-positive anaerobe, is the main cause of pulpal and periapical inflammation causing root canal failure. Literature evidence shows that the gold-standard calcium hydroxide is ineffective against E. faecalis due to its resistance to the alkaline pH and proton pump mechanism. Herbal essential oils such as oregano, basil, and thyme are known to possess antimicrobial properties against E. faecalis. However, their combination with calcium hydroxide as an intracanal medicament and the depth of penetration is still unknown. Aim To evaluate the depth of penetration of calcium hydroxide mixed with three different herbal essential oils using a confocal laser scanning microscope. Material and methods Fifty single-rooted premolars were decoronated and randomly divided into five groups. Group 1 - Oregano oil with calcium hydroxide, Group 2 - Basil oil with Calcium hydroxide, Group 3 - Thyme oil with calcium hydroxide, Group 4 - Calcium hydroxide with saline, Group 5 - Negative control. The teeth were instrumented and inoculated with E. faecalis and incubated for 21 days. Calcium hydroxide mixed with respective oils or saline and 0.1% rhodamine B dye was placed in the canals and again incubated for 7 days. Two sections each of 1 mm were horizontally cut at 3 mm and 5 mm from the apex and later subjected to a confocal laser scanning microscope to evaluate the depth of penetration. One-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test, and student t-test were performed. Results At the middle third, basil oil had the maximum depth of penetration (1377.47±14.1 µm) followed by oregano oil (1345.4±26.5 µm) and thyme oil (1160.4±24.6 µm). At apical third, basil oil (1152.4±31.6 µm) showed maximum depth of penetration, followed by thyme (988.3±26.2 µm) and oregano oils (419.5±19.8 µm). The depth of penetration of these oils was greater at the middle third than at the apical third. Conclusion Basil, oregano, and thyme oil have good penetration depth into the dentinal tubules and can be successfully used in root canal procedures as intracanal medicaments.
Keywords: basil oil; depth of penetration; e. faecalis; intracanal medicaments; oregano oil; thyme oil.
Copyright © 2024, Chandrasekaran et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Tagore Dental College and Hospital issued approval IEC/TDCH/154/2022. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
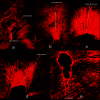
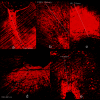
Similar articles
-
Assessment of depth of penetration and antibiofilm properties of Boswellia sacra compared with calcium hydroxide intracanal medicament (in vitro study).Aust Endod J. 2023 Aug;49(2):295-301. doi: 10.1111/aej.12675. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Aust Endod J. 2023. PMID: 36004503
-
Effect of Different Irrigant Activation Techniques on the Penetration of Calcium Hydroxide, an Intracanal Medicament: An In Vitro Study.Cureus. 2023 Nov 13;15(11):e48768. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48768. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38098913 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Penetration of Various Nano-sized Intra-canal Medicaments: An In Vitro Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopic Study.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024 Apr;16(Suppl 2):S1690-S1694. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_942_23. Epub 2024 Apr 16. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024. PMID: 38882763 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative assessment of nanosized intracanal medicaments on penetration and fracture resistance of root dentin - An in vitro study.J Conserv Dent Endod. 2024 Jan;27(1):17-23. doi: 10.4103/JCDE.JCDE_138_23. Epub 2024 Jan 13. J Conserv Dent Endod. 2024. PMID: 38389744 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Efficacy of Aloe vera, Lemon, Ricinus communis, and Calcium Hydroxide as Intracanal Medicament Against Enterococcus faecalis: A Confocal Microscopic Study.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2019 May;11(Suppl 2):S256-S259. doi: 10.4103/JPBS.JPBS_5_19. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2019. PMID: 31198348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Comparative evaluation of micron- and nano-sized intracanal medicaments on penetration and fracture resistance of root dentin - an in vitro study. Sireesha A, Jayasree R, Vidhya S, Mahalaxmi S, Sujatha V, Kumar TS. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;104:1866–1873. - PubMed
-
- Enterococcus faecalis: its role in root canal treatment failure and current concepts in retreatment. Stuart CH, Schwartz SA, Beeson TJ, Owatz CB. J Endod. 2006;32:93–98. - PubMed
-
- Association of Enterococcus faecalis with different forms of periradicular diseases. Rôças IN, Siqueira JF Jr, Santos KR. J Endod. 2004;30:315–320. - PubMed
-
- Antimicrobial efficacy of commercially available plant essential oils with calcium hydroxide as intracanal medicaments against Enterococcus faecalis: an in-vitro study. Tiwari G, Patil S, Bondarde P, Khadke S, Gakhare R. https://www.iosrjournals.org/iosr-jdms/papers/Vol17-issue6/Version-3/E17... IOSR J Dent Med Sci. 2018;17:19–24.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
