Whipple's Disease Endocarditis Following Immunomodulatory Treatment for Arthritis: A Case Report and Screening Recommendation
- PMID: 39310504
- PMCID: PMC11415841
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.67472
Whipple's Disease Endocarditis Following Immunomodulatory Treatment for Arthritis: A Case Report and Screening Recommendation
Abstract
Whipple's disease (WD) is a rare systemic disorder affecting various organ systems, including the gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, and joint systems. This report discusses a case of WD endocarditis likely associated with tocilizumab (TCZ), an immunomodulator used to treat refractory seronegative arthritis, in a patient with coronary artery disease and rheumatoid arthritis. The diagnosis was confirmed through laboratory studies, imaging, and esophagogastroduodenoscopy with biopsies. WD is increasingly recognized as a potential etiology of seronegative arthritis, with joint pain often preceding gastrointestinal symptoms. Immunomodulatory agents such as TCZ, while effective for rheumatoid arthritis, may exacerbate underlying WD, potentially leading to severe complications such as endocarditis. This case reveals the importance of considering WD in patients with refractory arthritis and the necessity of thorough diagnostic evaluation before initiating immunomodulatory therapy. Epidemiological studies indicate a higher prevalence of WD in certain demographics, highlighting the need for targeted screening with noninvasive screening methodologies, such as stool and saliva polymerase chain reaction testing.
Keywords: blood culture-negative endocarditis; endocarditis tropheryma whipplei; infective endocarditis; seronegative arthritis; tocilizumab; tropheryma whipplei; whipple’s disease.
Copyright © 2024, Back et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
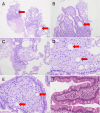
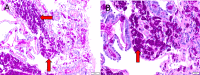
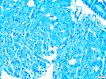
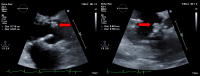
Similar articles
-
Tropheryma whipplei and Whipple's disease.J Infect. 2014 Aug;69(2):103-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2014.05.008. Epub 2014 May 28. J Infect. 2014. PMID: 24877762 Review.
-
Arthralgia and blood culture-negative endocarditis in middle Age Men suggest tropheryma whipplei infection: report of two cases and review of the literature.BMC Infect Dis. 2015 Aug 18;15:339. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1078-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26282628 Free PMC article.
-
Whipple's disease mimicking rheumatoid arthritis can cause misdiagnosis and treatment failure.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017 May 25;12(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s13023-017-0630-4. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017. PMID: 28545554 Free PMC article.
-
[The rich diversity of Whipple's disease].Z Rheumatol. 2019 Feb;78(1):55-65. doi: 10.1007/s00393-018-0573-8. Z Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30552512 Review. German.
-
Seronegative Arthritis as a Complication of Whipple's Disease.Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2021 May 17;14:11795476211017717. doi: 10.1177/11795476211017717. eCollection 2021. Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34045913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antunes C, Singhal M. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Whipple Disease. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
