Artificial Intelligence-What to Expect From Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Hernia Surgery
- PMID: 39310669
- PMCID: PMC11412881
- DOI: 10.3389/jaws.2024.13059
Artificial Intelligence-What to Expect From Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Hernia Surgery
Abstract
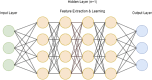
This mini-review explores the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) within hernia surgery, highlighting the role of Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL). The term AI incorporates various technologies including ML, Neural Networks (NN), and DL. Classical ML algorithms depend on structured, labeled data for predictions, requiring significant human oversight. In contrast, DL, a subset of ML, generally leverages unlabeled, raw data such as images and videos to autonomously identify patterns and make intricate deductions. This process is enabled by neural networks used in DL, where hidden layers between the input and output capture complex data patterns. These layers' configuration and weighting are pivotal in developing effective models for various applications, such as image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and more specifically, surgical procedures and outcomes in hernia surgery. Significant advancements have been achieved with DL models in surgical settings, particularly in predicting the complexity of abdominal wall reconstruction (AWR) and other postoperative outcomes, which are elaborated in detail within the context of this mini-review. The review method involved analyzing relevant literature from databases such as PubMed and Google Scholar, focusing on studies related to preoperative planning, intraoperative techniques, and postoperative management within hernia surgery. Only recent, peer-reviewed publications in English that directly relate to the topic were included, highlighting the latest advancements in the field to depict potential benefits and current limitations of AI technologies in hernia surgery, advocating for further research and application in this evolving field.
Keywords: AI; deep learning; hernia surgery; machine learning; neural network.
Copyright © 2024 Vogel and Mück.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deep convolutional neural network and IoT technology for healthcare.Digit Health. 2024 Jan 17;10:20552076231220123. doi: 10.1177/20552076231220123. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 38250147 Free PMC article.
-
Data-driven modeling and prediction of blood glucose dynamics: Machine learning applications in type 1 diabetes.Artif Intell Med. 2019 Jul;98:109-134. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2019.07.007. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Artif Intell Med. 2019. PMID: 31383477 Review.
-
Current advances in the use of artificial intelligence in predicting and managing urological complications.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Nov;56(11):3427-3435. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04149-8. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38982018 Review.
-
Role of artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning models in corneal disorders - A narrative review.J Fr Ophtalmol. 2024 Sep;47(7):104242. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2024.104242. Epub 2024 Jul 15. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2024. PMID: 39013268 Review.
-
The Role of AI in Modern Hernia Surgery: A Review and Practical Insights.Surg Innov. 2025 Jun;32(3):301-311. doi: 10.1177/15533506251328481. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Surg Innov. 2025. PMID: 40104921 Review.
References
-
- School of Mathematics and Statistics. Quotations by Alan Turing. United Kingdom: University of St Andrews; (2024). Available from: https://mathshistory.st-andrews.ac.uk/Biographies/Turing/quotations/ (Accessed July 02, 2024).
-
- Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Artificial Intelligence. Chicago, IL, United States: Encyclopædia Britannica; (2024). Available from: https://www.britannica.com/technology/artificial-intelligence/Alan-Turin... (Accessed July 02, 2024).
-
- Bell J. What Is Machine Learning? In: Machine Learning and the City: Applications in Architecture and Urban Design (2022). p. 207–16.
-
- Hassan AM, Lu SC, Asaad M, Liu J, Offodile AC, Sidey-Gibbons C, et al. Novel Machine Learning Approach for the Prediction of Hernia Recurrence, Surgical Complication, and 30-Day Readmission After Abdominal Wall Reconstruction. J Am Coll Surg (2022) 234(5):918–27. 10.1097/XCS.0000000000000141 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources