Dissimilar Planes and Approaches with Common Neural Targets - A Cadaveric Evaluation of Three Different Ultrasound-guided Fascial Plane Blocks for Lumbar Plexus Nerves
- PMID: 39310877
- PMCID: PMC11414952
- DOI: 10.4103/jmu.jmu_70_23
Dissimilar Planes and Approaches with Common Neural Targets - A Cadaveric Evaluation of Three Different Ultrasound-guided Fascial Plane Blocks for Lumbar Plexus Nerves
Abstract
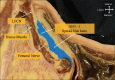
Background: The lumbar plexus (LP) is a group of nerves located at the fourth lumbar vertebra level, between the anterior two-thirds and posterior one-thirds of the psoas muscle. In this study, the researchers aimed to investigate the spread of latex in injections of LP, suprainguinal fascia iliaca, and circum-psoas planes to assess the different regional techniques for blocking LP nerves (LPNs).
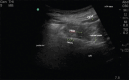
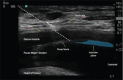
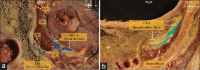
Methods: The study involved performing ultrasound-guided injections of three different colored latexes in six cadavers. The researchers observed and compared the spread of latex in each plane by taking cross sections at the levels of L4, anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS), and sacral foramina (SF). The spread of latex and LPN staining was documented and analyzed through photography.
Results: The results showed that the latex spread within the psoas muscle and fascia iliaca plane (FIP) during LP injections, whereas suprainguinal fascia iliaca injections showed latex dissemination in the FIP at both ASIS and SF levels. On the other hand, circum-psoas injections spread beneath the iliopsoas fascia at both levels and medially toward the external iliac vessels. Despite this spread, there was no communication between the three planes, and there was no mixing of latex from the different injections at any level.
Conclusion: There are distinct fascial planes, for the three approaches, with no communication between them. While latex diffused from LP plane to FIP, no mixing of dye was observed and also the reverse could not be achieved. These findings suggest that different regional techniques for blocking LPNs have their unique planes of action.
Keywords: Fascial planes block; lumbar plexus nerves block; peripheral nerve block; regional nerve block; ultrasound-guided block.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Medical Ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Anatomic evaluation to compare the dye spread with ultrasound-guided pericapsular nerve group (PENG) injection with or without an additional suprainguinal fascia iliaca (SIFI) injection in soft embalmed cadavers.J Anesth. 2024 Aug;38(4):445-454. doi: 10.1007/s00540-024-03333-5. Epub 2024 Mar 11. J Anesth. 2024. PMID: 38466404
-
The Pathway of Injectate Spread With the Transmuscular Quadratus Lumborum Block: A Cadaver Study.Anesth Analg. 2017 Jul;125(1):303-312. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001922. Anesth Analg. 2017. PMID: 28277325
-
The effect of the volume of supra-inguinal injected solution on the spread of the injectate under the fascia iliaca: a preliminary study.J Anesth. 2018 Dec;32(6):908-913. doi: 10.1007/s00540-018-2558-9. Epub 2018 Sep 24. J Anesth. 2018. PMID: 30250982
-
Understanding fascial anatomy and interfascial communication: implications in regional anesthesia.J Anesth. 2022 Aug;36(4):554-563. doi: 10.1007/s00540-022-03082-3. Epub 2022 Jun 13. J Anesth. 2022. PMID: 35697947 Review.
-
Anesthesiologists ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia core curriculum: a Delphi consensus from Italian regional anesthesia experts.J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2024 Aug 10;4(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s44158-024-00190-2. J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 39127723 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mannion S, Barrett J, Kelly D, Murphy DB, Shorten GD. A description of the spread of injectate after psoas compartment block using magnetic resonance imaging. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2005;30:567–71. - PubMed
-
- Desmet M, Vermeylen K, Van Herreweghe I, Carlier L, Soetens F, Lambrecht S, et al. Alongitudinal supra-inguinal fascia iliaca compartment block reduces morphine consumption after total hip arthroplasty. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2017;42:327–33. - PubMed
-
- Feigl GC, Dreu M, Ulz H, Breschan C, Maier C, Likar R. Susceptibility of the genitofemoral and lateral femoral cutaneous nerves to complications from lumbar sympathetic blocks: Is there a morphological reason? Br J Anaesth. 2014;112:1098–104. - PubMed
-
- Bendtsen TF, Pedersen EM, Moriggl B, Hebbard P, Ivanusic J, Børglum J, et al. Anatomical considerations for obturator nerve block with fascia iliaca compartment block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021;46:806–12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
