Roles of the NR2F Family in the Development, Disease, and Cancer of the Lung
- PMID: 39311119
- PMCID: PMC11417824
- DOI: 10.3390/jdb12030024
Roles of the NR2F Family in the Development, Disease, and Cancer of the Lung
Abstract
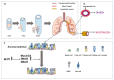
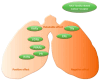
The NR2F family, including NR2F1, NR2F2, and NR2F6, belongs to the nuclear receptor superfamily. NR2F family members function as transcription factors and play essential roles in the development of multiple organs or tissues in mammals, including the central nervous system, veins and arteries, kidneys, uterus, and vasculature. In the central nervous system, NR2F1/2 coordinate with each other to regulate the development of specific brain subregions or cell types. In addition, NR2F family members are associated with various cancers, such as prostate cancer, breast cancer, and esophageal cancer. Nonetheless, the roles of the NR2F family in the development and diseases of the lung have not been systematically summarized. In this review, we mainly focus on the lung, including recent findings regarding the roles of the NR2F family in development, physiological function, and cancer.
Keywords: NR2F family; carcinogenesis; lung; nuclear receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New Insights into the Diverse Functions of the NR2F Nuclear Orphan Receptor Family.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Jan 17;28(1):13. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2801013. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 36722280 Review.
-
Origin and evolutionary landscape of Nr2f transcription factors across Metazoa.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 22;16(11):e0254282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254282. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34807940 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of nr2f genes in brain regionalization and eye development during early zebrafish development.Dev Growth Differ. 2024 Feb;66(2):145-160. doi: 10.1111/dgd.12912. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Dev Growth Differ. 2024. PMID: 38263801 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and retinoic acid regulation of the zebrafish nr2f orphan nuclear receptor genes.Dev Dyn. 2012 Oct;241(10):1603-15. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.23838. Epub 2012 Aug 13. Dev Dyn. 2012. PMID: 22836912 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptors in Leydig cell gene expression and function.Biol Reprod. 2010 Jul;83(1):3-14. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.083824. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Biol Reprod. 2010. PMID: 20375256 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Highly Variable Expressivity of a CNV Deletion Involving TBX4 in Three Deceased Siblings With Lung Developmental Disorder and Their Mildly Affected Mother and Grandfather.Clin Genet. 2025 Jun 21:10.1111/cge.70010. doi: 10.1111/cge.70010. Online ahead of print. Clin Genet. 2025. PMID: 40542660
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

