Pregnenolone 16-Alpha Carbonitrile, an Agonist of Rodent Pregnane X Receptor, Regulates Testosterone Biosynthesis in Rodent Leydig Cells
- PMID: 39311150
- PMCID: PMC11417858
- DOI: 10.3390/jox14030071
Pregnenolone 16-Alpha Carbonitrile, an Agonist of Rodent Pregnane X Receptor, Regulates Testosterone Biosynthesis in Rodent Leydig Cells
Abstract
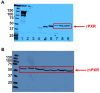
Leydig cells (LCs) in the testes produce the male sex hormone testosterone (T). Several xenobiotics, including clinical drugs, supplements, and environmental chemicals, are known to disrupt T homeostasis. Notably, some of these xenobiotics are known to activate the pregnane X receptor (PXR), a ligand-dependent nuclear receptor. However, it is currently unknown whether PXR is expressed in LCs and whether PXR activation alters T synthesis in rodent LCs. Therefore, in this study, we sought to determine whether PXR is expressed in rodent LCs and whether pregnenolone 16-alpha carbonitrile (PCN), the prototype agonist of rodent PXR, regulates T biosynthesis in rodent LCs. Hormonal as well as protein and gene expression analyses were conducted in rat primary LCs and MA-10 mouse Leydig cells. Results showed that PXR was expressed at the mRNA and protein level in both rat primary LCs and MA-10 cells. Incubation of rat primary LCs with PCN resulted in a significant decrease in T secretion. This PCN-induced decrease in T secretion was associated with decreased protein expression of key steroidogenic enzymes such as 3β-HSD and CYP17A1. RNA-seq results from MA-10 cells showed that PCN down-regulated the transcripts of steroidogenic enzymes and proteins involved in the T synthesis pathway. Together, these results suggest that PCN, an agonist of rodent PXR, can regulate T biosynthesis in rodent LCs by down-regulating the expression of the steroidogenic enzymes involved in T biosynthesis. Our results are significant as they provide a potential novel mechanism for disruption of testosterone homeostasis by a variety of xenobiotics.
Keywords: Leydig cells; MA-10 cells; pregnane X receptor (PXR); pregnenolone 16-alpha carbonitrile (PCN); testis; testosterone; xenobiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Gut Microbiota Affects Mouse Pregnane X Receptor Agonist Pregnenolone 16α-Carbonitrile-Induced Hepatomegaly by Regulating Pregnane X Receptor and Yes-Associated Protein Activation.Drug Metab Dispos. 2024 Jun 17;52(7):597-605. doi: 10.1124/dmd.123.001604. Drug Metab Dispos. 2024. PMID: 38697851
-
Comparison of the hepatic and thyroid gland effects of sodium phenobarbital in wild type and constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) knockout rats and pregnenolone-16α-carbonitrile in wild type and pregnane X receptor (PXR) knockout rats.Toxicology. 2018 May 1;400-401:20-27. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Toxicology. 2018. PMID: 29548889
-
The Pregnane-X receptor regulates steroid synthesis in mouse Leydig cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 May 6;15:1430781. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1430781. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40395611 Free PMC article.
-
Rodent Leydig cell tumorigenesis: a review of the physiology, pathology, mechanisms, and relevance to humans.Crit Rev Toxicol. 1999 Mar;29(2):169-261. doi: 10.1080/10408449991349203. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1999. PMID: 10213111 Review.
-
Pregnane X receptor: molecular basis for species differences in CYP3A induction by xenobiotics.Chem Biol Interact. 2001 May 16;134(3):283-9. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(01)00163-6. Chem Biol Interact. 2001. PMID: 11336976 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Cytochrome P450 Cancer-Related Metabolic Activities and Gene Polymorphisms: A Review.Cells. 2024 Nov 26;13(23):1958. doi: 10.3390/cells13231958. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39682707 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

