Content, Behaviour Change Techniques, and Quality of Postpartum Depression Apps to Be Recommended by Midwives: Systematic Search and Evaluation
- PMID: 39311178
- PMCID: PMC11435284
- DOI: 10.3390/nursrep14030170
Content, Behaviour Change Techniques, and Quality of Postpartum Depression Apps to Be Recommended by Midwives: Systematic Search and Evaluation
Abstract
Background: Postpartum depression is a public health problem that affects a considerable percentage of women. Despite the proliferation of related apps, there are limited data available on the best apps to prevent postpartum depression. We identified which apps available in Spanish could be recommended by midwives based on their content, quality, and behaviour change techniques, as a complementary tool for preventing postpartum depression in women.
Methods: A systematic search was performed to identify apps available on iOS App Store and Google Play, which were used to replicate how patients' access "postpartum depression prevention" apps. Apps' quality, behaviour change potential, and contents were assessed.
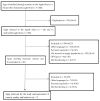
Results: A total of 1408 apps were identified, of which 7 were retrieved for assessment (0.5%). The mean objective and subject quality were 3.1 (SD = 1.01) and 2.7 (SD = 1.27), respectively. A total of 24 topics were identified. The mean ABACUS score was 6.6 (SD = 3.64), and the mean number of topics addressed by the apps was 9.9 (SD = 5.90).
Conclusion: The results of the present study suggest that a specific free app is not available in Spanish for the prevention of postpartum depression, and only a small percentage of free apps should be recommended based on their quality, BCTs, and contents. The systematic review protocol was not registered.
Keywords: health promotion; mobile health; postpartum depression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Similar articles
-
Assessment of content, behavior change techniques, and quality of unintended pregnancy apps in Spain: Systematic search on app stores.Digit Health. 2023 May 11;9:20552076231173563. doi: 10.1177/20552076231173563. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2023. PMID: 37197412 Free PMC article.
-
Content, Behavior Change Techniques, and Quality of Pregnancy Apps in Spain: Systematic Search on App Stores.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2021 Nov 17;9(11):e27995. doi: 10.2196/27995. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2021. PMID: 34787587 Free PMC article.
-
Quality, Features, and Presence of Behavior Change Techniques in Mobile Apps Designed to Improve Physical Activity in Pregnant Women: Systematic Search and Content Analysis.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2021 Apr 7;9(4):e23649. doi: 10.2196/23649. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2021. PMID: 33825693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Most Popular Commercial Weight Management Apps in the Chinese App Store: Analysis of Quality, Features, and Behavior Change Techniques.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2023 Nov 24;11:e50226. doi: 10.2196/50226. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2023. PMID: 37999950 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Patient-Facing Mobile Apps to Support Physiotherapy Care: Systematic Review.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2024 Mar 4;12:e55003. doi: 10.2196/55003. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2024. PMID: 38437018 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Validation of a Questionnaire Assessing Pregnant Women's Perspectives on Addressing the Psychological Challenges of Childbirth.Nurs Rep. 2024 Dec 31;15(1):8. doi: 10.3390/nursrep15010008. Nurs Rep. 2024. PMID: 39852630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Maternal Mental Health. [(accessed on 30 January 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/mental-health-and-substance-use/promotion-prev....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources