CO2-Free On-Stage Incubator for Live Cell Imaging of Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Migration on Microfluidic Device
- PMID: 39311370
- PMCID: PMC11417791
- DOI: 10.3390/mps7050069
CO2-Free On-Stage Incubator for Live Cell Imaging of Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Migration on Microfluidic Device
Abstract
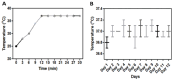
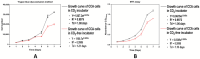
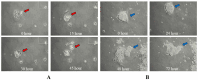
Long-term live cell imaging requires sophisticated and fully automated commercial-stage incubators equipped with specified inverted microscopes to regulate temperature, CO2 content, and humidity. In this study, we present a CO2-free on-stage incubator specifically designed for use across various cell culture platforms, enabling live cell imaging applications. A simple and transparent incubator was fabricated from acrylic sheets to be easily placed on the stages of most inverted microscopes. We successfully performed live-cell imaging of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) cells and HeLa cell dynamics in both 2D and 3D microenvironments over three days. We also analyzed directed cell migration under high serum induction within a microfluidic device. Interesting phenomena such as "whole-colony migration", "novel type of collective cell migration" and "colony formation during cell and colony migration" are reported here for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. These phenomena may improve our understanding of the nature of cell migration and cancer metastasis.
Keywords: cell migration; cholangiocarcinoma (CCA); live-cell imaging; microfluidics; on-stage incubator.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures


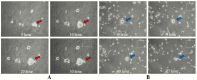

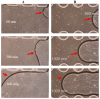
Similar articles
-
Facilitating long-term cell examinations and time-lapse recordings in cell biology research with CO2 mini-incubators.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 10;14(1):3418. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52866-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38341451 Free PMC article.
-
A Passive Microfluidic Device for Chemotaxis Studies.Micromachines (Basel). 2019 Aug 20;10(8):551. doi: 10.3390/mi10080551. Micromachines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31434220 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of the microscope incubation system and its application in evaluating tumor treatment effects through real-time live cellular imaging.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 16;12:1447265. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1447265. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39219621 Free PMC article.
-
Incubator-independent perfusion system integrated with microfluidic device for continuous electrophysiology and microscopy readouts.Biofabrication. 2023 Feb 2;15(2). doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/acb466. Biofabrication. 2023. PMID: 36652708
-
Decisions for the IVF laboratory: comparative analysis of embryo culture incubators.Reprod Biomed Online. 2014 May;28(5):535-47. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2014.01.004. Epub 2014 Jan 27. Reprod Biomed Online. 2014. PMID: 24656561 Review.
Cited by
-
Applications of 3D models in cholangiocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 31;15:1598552. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1598552. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40823086 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ragazzini G., Mescola A., Corsi L., Alessandrini A. Fabrication of a low-cost on-stage cell incubator with full automation. J. Biol. Educ. 2019;53:165–173. doi: 10.1080/00219266.2018.1451772. - DOI
-
- Peter B., Nador J., Juhasz K., Dobos A., Korosi L., Székács I., Patko D., Horvath R. Incubator proof miniaturized Holomonitor to in situ monitor cancer cells exposed to green tea polyphenol and preosteoblast cells adhering on nanostructured titanate surfaces: Validity of the measured parameters and their corrections. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015;20:067002. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.20.6.067002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- King S.J., Parsons M. Cell Migration. Humana Press; Totowa, NJ, USA: 2011. Imaging cells within 3D cell-derived matrix; pp. 53–64. - PubMed
-
- [(accessed on 14 August 2024)]. Available online: https://www.wpi-europe.com/products/microscopes-and,cameras/miscellaneou....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

